20 Of 460
stanleys
Sep 15, 2025 · 6 min read
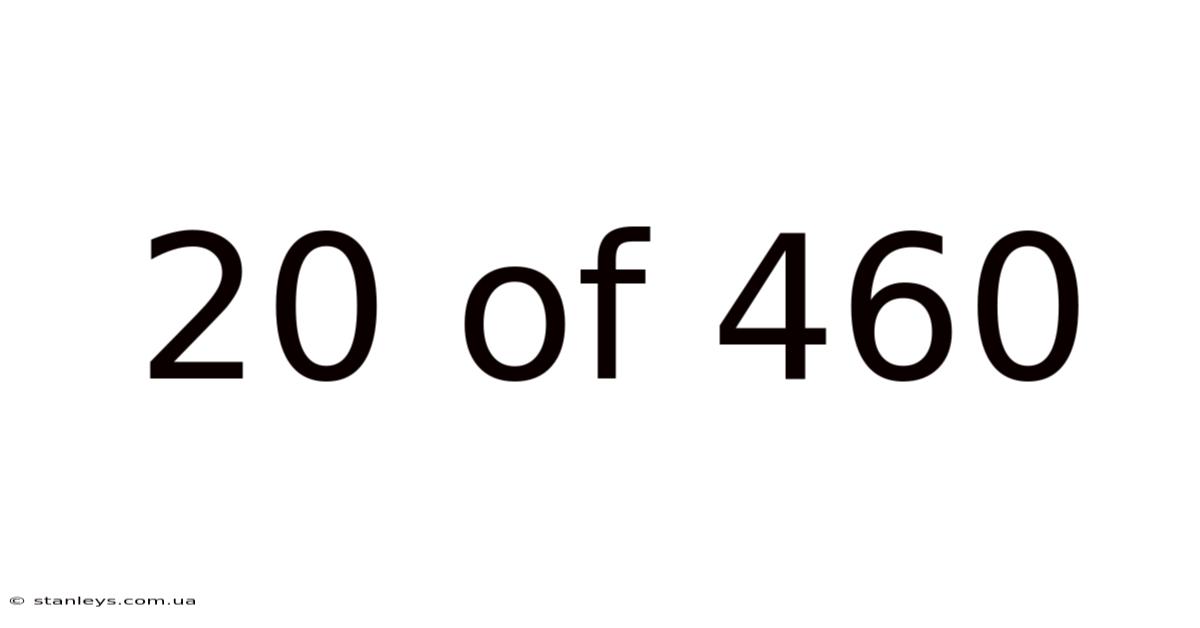
Table of Contents
Decoding the Enigma: Understanding the Significance of 20 out of 460
The seemingly simple fraction, 20 out of 460, can represent a multitude of scenarios, from test scores to survey results, and even complex scientific data. Understanding its significance requires delving deeper than just the raw numbers. This article will explore the various interpretations of this fraction, providing tools and techniques for analysis, and ultimately empowering you to understand the context and implications of such data. We will cover how to calculate percentages, interpret the results within different contexts, and even delve into the potential statistical significance depending on the underlying situation.
Introduction: Beyond the Numbers
At first glance, 20 out of 460 might seem insignificant. However, the true meaning depends entirely on the context. Imagine these scenarios:
- Scenario 1: A student scores 20 out of 460 on a major exam. This paints a picture of poor performance.
- Scenario 2: A researcher observes 20 positive outcomes out of 460 trials in a medical experiment. The interpretation here is far more nuanced and requires statistical analysis.
- Scenario 3: A company receives 20 positive customer reviews out of 460 total reviews. This suggests customer satisfaction levels requiring attention.
These diverse scenarios highlight the importance of considering the context before making any judgments based solely on the numbers. This article will provide a framework for analyzing such data regardless of its source.
Calculating the Percentage: A Fundamental Step
The first step in understanding the significance of 20 out of 460 is to calculate the percentage. This provides a standardized way to compare this ratio to other similar ratios. The calculation is straightforward:
(20 / 460) * 100% = 4.35%
This means that 20 represents approximately 4.35% of 460. This percentage provides a clearer, more concise representation of the proportion than the raw numbers alone.
Interpreting the Percentage in Different Contexts
The interpretation of 4.35% depends heavily on the context:
-
Academic Performance: In the context of a major exam, 4.35% is a very low score, indicating a significant need for improvement. The grading scale and the difficulty of the exam would further contextualize this result.
-
Scientific Research: In a medical experiment, 4.35% success rate might be considered low, high, or somewhere in between, depending on the established benchmarks for similar experiments and the nature of the treatment or intervention being tested. Further statistical analysis (like a confidence interval or p-value) is crucial for drawing reliable conclusions.
-
Customer Feedback: A 4.35% positive customer review rate suggests a significant problem with customer satisfaction. The company needs to investigate the reasons behind the low ratings and implement improvements to enhance the customer experience.
-
Quality Control: In a manufacturing process, 4.35% defect rate may or may not be acceptable, depending on the industry standards and the cost of defects.
Deeper Dive: Statistical Significance
In scenarios involving scientific research, surveys, or quality control, understanding the statistical significance of the 20 out of 460 result is crucial. We need to consider factors like:
-
Sample Size: 460 might be a large enough sample size for some applications, ensuring a reasonable level of confidence in the results. However, for others, it might not be sufficient to draw definitive conclusions.
-
Margin of Error: The margin of error is related to the sample size. A larger sample size will usually lead to a smaller margin of error, providing more precise results.
-
Statistical Tests: Depending on the research question and data type, various statistical tests can be employed to determine if the observed result is statistically significant (meaning the result is unlikely due to random chance). Chi-square tests, z-tests, or t-tests are examples that could be relevant.
-
Confidence Intervals: Instead of simply reporting the percentage, a confidence interval provides a range of values within which the true population percentage is likely to lie. For example, a 95% confidence interval might be 2% to 7%, indicating there's a 95% probability that the true percentage lies within this range.
Practical Applications and Examples
Let's explore some real-world applications illustrating the importance of context:
Example 1: Clinical Trials
A pharmaceutical company conducts a clinical trial testing a new drug. Out of 460 participants, 20 experience a significant improvement in their condition. While the 4.35% success rate appears low, a thorough statistical analysis is crucial. Factors such as the severity of the condition, the placebo effect, and the sample size need careful consideration before drawing conclusions.
Example 2: Marketing Campaign Analysis
A company launches a new marketing campaign targeting 460 potential customers. Only 20 make a purchase. This low conversion rate (4.35%) suggests the campaign was ineffective and requires revisions. Analysis of the target audience, the campaign's messaging, and the chosen channels are essential for identifying areas for improvement.
Example 3: Manufacturing Quality Control
A factory produces 460 units of a product, and 20 are found to be defective. This 4.35% defect rate needs to be examined against acceptable industry standards. If the cost of defects is high, even a seemingly small percentage may require significant action to improve the production process.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How can I calculate the confidence interval for 20 out of 460?
A: Calculating a confidence interval requires using statistical software or calculators and involves specifying a confidence level (e.g., 95%). The calculation depends on whether you are using a proportions z-test or another appropriate statistical method.
Q: What statistical tests are suitable for analyzing data like this?
A: The appropriate statistical test depends on the research question and the type of data. If you are comparing proportions, a z-test for proportions might be suitable. If dealing with categorical data, a chi-square test might be more appropriate.
Q: What if the sample size were smaller, say, 46 instead of 460?
A: With a smaller sample size, the margin of error increases, making it more challenging to draw reliable conclusions. The results might be less statistically significant.
Q: Is 4.35% always a low percentage?
A: Not necessarily. The significance of 4.35% is entirely dependent on the context. In some situations, it might be considered high, while in others it might be extremely low.
Conclusion: Context is King
The seemingly simple ratio of 20 out of 460 translates to 4.35%. However, its interpretation is far from simple and hinges entirely on the context. Understanding the percentage alone is insufficient. A deeper analysis, incorporating statistical methods, considering the sample size, and evaluating the implications within the specific scenario are critical for arriving at meaningful and accurate conclusions. By understanding these principles, you can move beyond simply recognizing the numbers and gain valuable insights from even seemingly small proportions. Always remember that context is king when analyzing data. The true story lies not just in the numbers themselves, but in the story they tell within their specific domain.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
X 2 4x
Sep 15, 2025
-
0 07 In Fraction
Sep 15, 2025
-
Ashfields Polo Club
Sep 15, 2025
-
Opposite To Gentle
Sep 15, 2025
-
38 8f To C
Sep 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 20 Of 460 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.