10000 X 1000
stanleys
Sep 15, 2025 · 5 min read
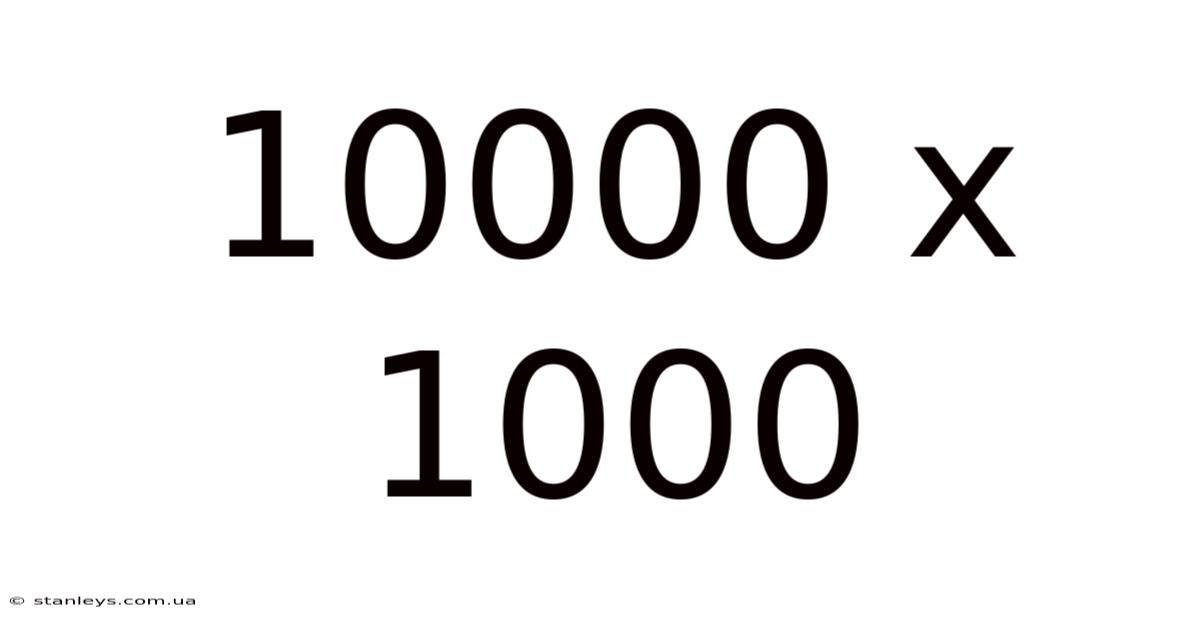
Table of Contents
Decoding 10,000 x 10,000: A Deep Dive into Scale, Implications, and Applications
The seemingly simple multiplication problem of 10,000 x 10,000 might appear trivial at first glance. However, unpacking this calculation reveals profound implications across various fields, from data science and computer science to geography and economics. This article will delve into the meaning of this calculation, explore its applications, and uncover the fascinating concepts it represents. We'll move beyond the simple answer (100,000,000) to understand the magnitude and significance of this number within different contexts.
Understanding the Magnitude: Beyond the Numbers
The result of 10,000 x 10,000, which is 100,000,000 (one hundred million), is not just a large number; it represents a significant scale. To grasp this magnitude, consider the following:
-
Population Scale: 100 million people represent a substantial population, comparable to the populations of several large countries. This scale is relevant in demographic studies, resource allocation, and understanding societal structures.
-
Data Storage: In the realm of computing, 100 million represents a significant amount of data. Think of 100 million images, documents, or data points. This scale necessitates efficient data storage solutions and powerful processing capabilities.
-
Geographic Scale: Imagine a square area with sides of 10,000 units (meters, feet, etc.). This results in a vast area of 100 million square units. Such a scale is relevant in land management, urban planning, and environmental studies.
-
Financial Scale: 100 million dollars (or any other currency) represents a significant financial sum, impacting investment strategies, economic policies, and large-scale projects.
Applications in Different Fields: A Multifaceted Perspective
The 10,000 x 10,000 calculation and its result, 100 million, have wide-ranging applications across diverse fields. Let's explore some examples:
1. Computer Science and Data Science:
-
Image Processing: Processing images with a resolution of 10,000 x 10,000 pixels requires significant computational power. This resolution is used in high-resolution satellite imagery, medical imaging (e.g., high-resolution scans), and advanced microscopy. The sheer volume of data necessitates efficient algorithms and specialized hardware.
-
Big Data Analysis: Analyzing datasets with 100 million data points requires advanced techniques in big data analytics. This is crucial in fields like genomics, social media analysis, financial modeling, and weather forecasting. The scale of the data demands robust infrastructure and distributed computing approaches.
-
Machine Learning: Training sophisticated machine learning models often involves massive datasets. A 100-million data point dataset provides substantial training data for complex models, but also poses challenges in computational resources and time.
2. Geography and Mapping:
-
High-Resolution Mapping: Creating maps with a resolution of 10,000 x 10,000 pixels allows for incredibly detailed representations of geographical areas. This is vital for precision agriculture, environmental monitoring, urban planning, and disaster response.
-
Satellite Imagery Analysis: Satellite images with such high resolutions provide invaluable data for studying land use changes, environmental impacts, and urban development patterns. Processing and analyzing this data requires sophisticated techniques and powerful computing resources.
3. Economics and Finance:
-
Market Analysis: Analyzing vast financial datasets with 100 million data points can provide insights into market trends, investment opportunities, and risk assessment. This is crucial for financial institutions, investors, and economists.
-
Economic Modeling: Developing and testing complex economic models often involves simulating scenarios with numerous variables. The scale represented by 100 million can improve the accuracy and reliability of such models.
4. Engineering and Physics:
-
Simulation and Modeling: Many engineering and physics problems involve simulations with a vast number of parameters. The scale of 10,000 x 10,000 can be relevant in areas like fluid dynamics, climate modeling, and material science simulations.
-
High-Precision Measurements: In some scientific experiments, extremely high-precision measurements are required. The number 100 million might represent the number of data points collected during a specific experiment, demanding sophisticated data processing and analysis techniques.
Beyond the Calculation: Conceptual Implications
The 10,000 x 10,000 calculation extends beyond a simple arithmetic problem. It highlights several crucial concepts:
-
Scale and Magnitude: Understanding the scale represented by 100 million is critical across various disciplines. It emphasizes the importance of considering the magnitude of data, resources, and phenomena being studied.
-
Computational Complexity: Processing and analyzing data at this scale demands significant computational resources and sophisticated algorithms. Understanding computational complexity is crucial in developing efficient solutions for big data problems.
-
Data Management: Effective data management is critical when dealing with large datasets. This involves techniques for storage, retrieval, processing, and analysis of vast amounts of information.
-
System Design: Building systems capable of handling data at this scale necessitates careful system design, considering aspects such as scalability, reliability, and fault tolerance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the significance of using powers of 10?
A1: Using powers of 10 (10,000 = 10<sup>4</sup>) simplifies calculations and represents a clear scale. It makes it easier to conceptualize and compare magnitudes across different fields.
Q2: Are there real-world examples where 10,000 x 10,000 is directly applicable?
A2: While a direct application of 10,000 x 10,000 as a literal calculation might be rare, the scale it represents—100 million—is directly applicable in numerous fields as described above.
Q3: What are the limitations of using such large numbers in modeling and simulations?
A3: Using extremely large numbers in modeling can lead to computational limitations, increased processing time, and potential inaccuracies due to rounding errors or approximations. Careful consideration of these factors is essential.
Q4: How does this calculation relate to exponential growth?
A4: While this is a simple multiplication, it demonstrates the rapid growth that can occur when large numbers are multiplied. This is conceptually related to exponential growth, where quantities increase at an accelerating rate.
Conclusion: A Number with Profound Implications
The seemingly straightforward calculation of 10,000 x 10,000 reveals a much deeper significance. The resulting 100 million is not just a number; it is a symbol of scale, representing massive datasets, vast geographical areas, significant populations, and large financial sums. Understanding the implications of this scale is crucial across diverse fields, from computer science and data science to geography, economics, and engineering. By exploring this simple calculation, we uncover a rich tapestry of concepts and applications that highlight the importance of scale, computational complexity, and effective data management in our increasingly data-driven world. The number 100 million serves as a potent reminder of the magnitude of challenges and opportunities presented by the ever-expanding scope of data and computation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Musical Theatre Characteristics
Sep 15, 2025
-
55inches To Feet
Sep 15, 2025
-
89kgs In Stone
Sep 15, 2025
-
Que Pena English
Sep 15, 2025
-
23 X 12
Sep 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 10000 X 1000 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.