X 12 7
stanleys
Sep 16, 2025 · 7 min read
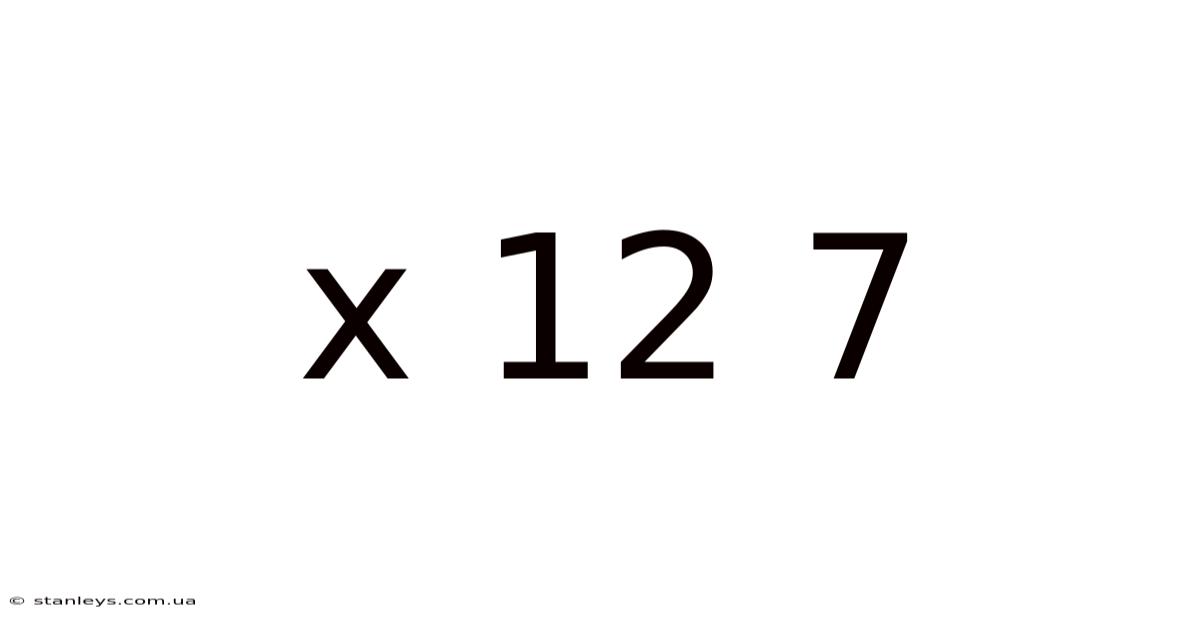
Table of Contents
Decoding X 12 7: A Deep Dive into Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
The seemingly simple expression "X12 7" actually represents a complex and crucial element within the world of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI). Understanding its significance requires delving into the fundamentals of EDI, its applications, and the specific role of the X12 standard, specifically transaction set 7. This article will provide a comprehensive overview, suitable for both beginners and those with some prior knowledge of EDI. We'll cover everything from the basics of EDI to the practical applications of X12 7, ensuring a clear and complete understanding of this vital component of modern business communication.
What is Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)?
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is the electronic exchange of business documents in a standardized format between trading partners. Instead of exchanging paper documents like purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notices, businesses use EDI to transmit these documents electronically. This automated process significantly improves efficiency, reduces errors, and speeds up transactions. Imagine the time and resources saved by eliminating manual data entry, printing, mailing, and faxing. EDI streamlines workflows and allows for seamless integration between different systems.
The Importance of Standards in EDI
The success of EDI relies heavily on standardized data formats. Without a common language, businesses would be unable to communicate effectively. Several standards exist, but one of the most widely used in North America is the ANSI ASC X12 standard. This standard defines the structure and content of various business documents, ensuring interoperability between different systems and organizations.
Understanding the ANSI ASC X12 Standard
ANSI ASC X12 is a comprehensive standard that encompasses numerous transaction sets, each designed for a specific business document. These transaction sets are identified by a numerical code. For example, 850 represents Purchase Orders, 856 represents Shipping Notices, and 810 represents Invoices. Each transaction set contains specific data elements, arranged in a predefined structure. This consistency allows businesses to seamlessly exchange data regardless of their internal systems.
X12 7: Functional Acknowledgement
Now, let's focus on "X12 7," which refers to the functional acknowledgement transaction set within the X12 standard. This is not a document representing a specific business process like a purchase order or invoice. Instead, it's a crucial control mechanism used to confirm the successful receipt and processing of other EDI transactions. Think of it as a digital receipt confirming that the sender's message has been received and processed by the recipient's system.
A functional acknowledgement doesn't provide detailed information about the contents of the original transaction. Its primary purpose is to verify that the message arrived without errors and was accepted for processing. This immediate feedback is vital for ensuring data integrity and preventing costly errors resulting from lost or corrupted messages.
The Mechanics of X12 7: How it Works
When a business sends an EDI transaction (like an 850 Purchase Order or an 810 Invoice) to its trading partner, the receiving system processes the document. If the system successfully processes the transaction – meaning it meets all formatting requirements, data validation rules, and internal processing constraints - it then generates and sends back an X12 7 functional acknowledgement.
This acknowledgement confirms that:
- The message was received: The receiving system confirms it successfully received the transmission.
- The message was processed: The receiving system confirms it processed the message according to its programmed rules. This doesn't necessarily mean the order is accepted or the invoice is correct, only that the message was handled without encountering any significant processing errors.
- The message's integrity: The receiving system confirms the message arrived complete and unaltered. If parts were missing or corrupted, the acknowledgment will likely reflect that.
Different Types of Functional Acknowledgements (997)
While generally referred to as "X12 7," the actual transaction set identifier for a functional acknowledgement is 997. The 997 can contain different levels of detail regarding the successful processing of the original transaction, allowing for various levels of confirmation. These levels can indicate whether there were minor errors that did not prevent processing or if significant errors prevented complete processing. Understanding the specific codes and meanings within the 997 is crucial for proper interpretation.
Importance of X12 7 in Error Prevention and Resolution
The immediate feedback provided by X12 7 is paramount in preventing data errors and facilitating quick resolution. If an error occurs during the initial transaction, the 997 will indicate the problem, allowing the sender to correct the issue promptly. This prevents delays, reduces costs associated with disputes and rework, and ultimately strengthens the trading relationship. Without the functional acknowledgement, errors might go undetected until much later, leading to significant complications and financial losses.
X12 7 and Different EDI Transaction Sets
The X12 7 (997) functional acknowledgement is not tied to a single transaction set. It can be used with any X12 transaction set. This means that regardless of whether you are sending purchase orders (850), invoices (810), or shipping notices (856), you can expect a 997 acknowledgement confirming successful receipt and processing. This universal applicability is a key strength of the X12 standard, ensuring consistent communication practices across diverse business transactions.
Implementing X12 7: Practical Considerations
Implementing X12 7 requires careful planning and coordination between trading partners. This involves:
- Agreement on the EDI standards: Trading partners need to agree on the specific X12 version and transaction sets to be used.
- Mapping of data elements: The system must be properly configured to map data elements between the sender's and receiver's systems.
- Testing and validation: Thorough testing and validation are crucial to ensure seamless communication and accurate interpretation of acknowledgements.
- Error handling procedures: Clear procedures must be defined for handling errors indicated in the 997 functional acknowledgement.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Concepts
While the core concept of X12 7 is straightforward, there are several advanced concepts related to functional acknowledgements that deserve mention:
- Implementation Guides: Detailed implementation guides exist to specify how to properly use the 997 transaction set. Understanding these guides is vital for effective implementation.
- Error Codes: The 997 uses specific codes to identify errors. Understanding these codes allows for prompt diagnosis and correction of issues.
- Security Considerations: When transmitting sensitive business data via EDI, security is paramount. Appropriate security measures should be implemented to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What happens if I don't receive a 997 acknowledgement? A: The absence of a 997 indicates a potential problem with the transmission or processing of the original transaction. Immediate investigation is required to identify the cause and re-transmit the message if necessary.
-
Q: Can I use X12 7 with other EDI standards? A: No, X12 7 (997) is specific to the ANSI ASC X12 standard. Other standards, such as EDIFACT, have their own mechanisms for acknowledging transactions.
-
Q: What should I do if I receive a 997 with error codes? A: Carefully review the error codes in the 997. These codes specify the type of error encountered. Correct the error in the original transaction and resubmit.
-
Q: Is X12 7 mandatory? A: While not legally mandated in most cases, using a functional acknowledgement like X12 7 is considered a best practice for ensuring reliable and error-free EDI transactions. It’s crucial for maintaining robust business relationships and preventing costly mistakes.
Conclusion
Understanding X12 7 (997) is essential for anyone involved in electronic data interchange. Its role in ensuring reliable communication, preventing errors, and streamlining business processes cannot be overstated. While the concept itself is relatively simple, the implementation and nuances require careful attention to detail. By understanding the principles outlined in this article, businesses can leverage the power of functional acknowledgements to improve their EDI operations and strengthen their relationships with trading partners. The seemingly simple "X12 7" represents a powerful tool in the modern business landscape, underpinning the efficient and reliable exchange of critical information.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 12 7 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.