25 Of 280
stanleys
Sep 10, 2025 · 6 min read
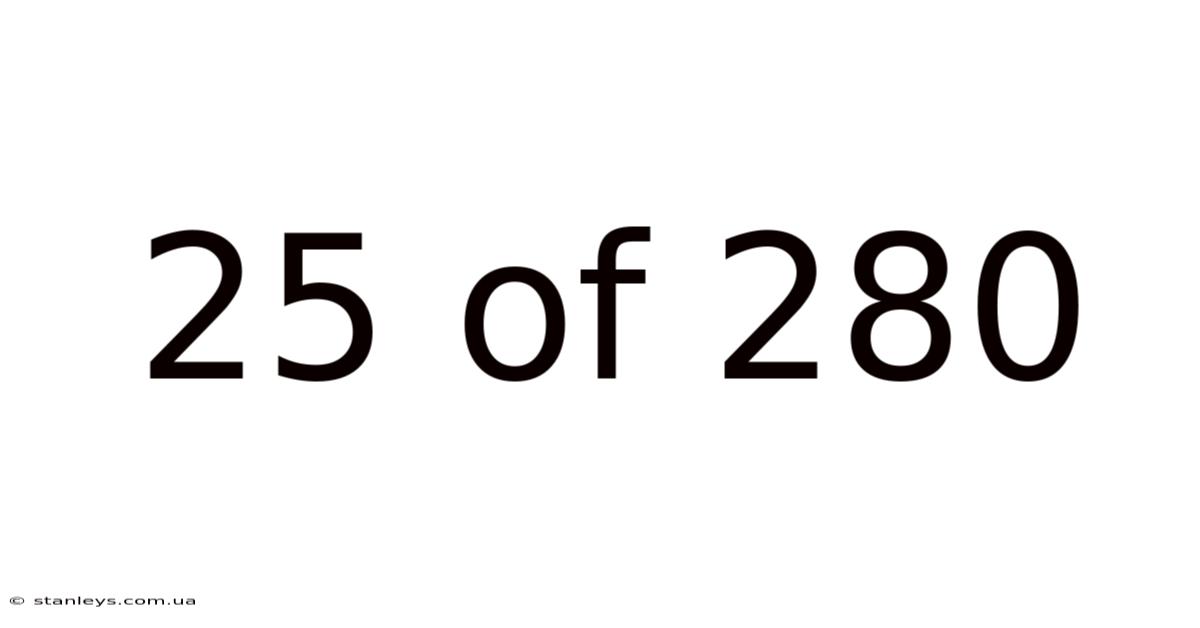
Table of Contents
Decoding the Enigma: Understanding the Significance of 25 out of 280
The seemingly simple fraction, 25 out of 280, can represent a wide range of scenarios, from academic performance to business metrics. Understanding its implications requires delving beyond the surface-level calculation and exploring the context in which this ratio appears. This article will dissect the meaning of this fraction, provide various interpretations, and explore the significance of understanding ratios in different contexts. We will examine methods for analyzing this data, delve into the importance of context, and explore related concepts to provide a complete understanding of its implications.
Understanding the Basic Calculation
The most straightforward approach to understanding "25 out of 280" is to express it as a fraction: 25/280. This fraction can then be simplified by finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of 25 and 280, which is 5. Dividing both the numerator and the denominator by 5, we obtain the simplified fraction 5/56.
This simplification helps in visualizing the proportion. We now know that 25 represents approximately 9% of 280. This percentage is calculated by dividing the numerator (25) by the denominator (280) and multiplying by 100: (25/280) * 100 ≈ 8.93%. This percentage provides a concise representation of the ratio's relative size.
Context is Key: Different Interpretations of 25/280
The true meaning of 25 out of 280 depends heavily on the context in which it arises. Here are some possible interpretations:
1. Academic Performance: Imagine 280 students took a test, and 25 scored above a certain threshold. In this case, 25/280 (or approximately 9%) represents the percentage of students who performed exceptionally well. This could be used to evaluate the overall class performance, identify areas for improvement in teaching methods, or even assess the difficulty of the test itself. Further analysis might involve comparing this percentage to past years' results or to the performance of other classes.
2. Business Metrics: Consider a scenario where a company sends out 280 marketing emails, and 25 result in a sale. Here, 25/280 (approximately 9%) represents the conversion rate of the email campaign. A low conversion rate might prompt the company to refine its marketing strategy, improve email content, or target a different audience. This data point alone is insufficient; it needs to be compared against previous campaign results and industry benchmarks to draw meaningful conclusions.
3. Quality Control: In a manufacturing process, if 280 units are produced, and 25 are found to be defective, then 25/280 (approximately 9%) represents the defect rate. This metric is crucial for quality control and identifying potential problems in the production line. A high defect rate might necessitate adjustments to the manufacturing process, stricter quality checks, or even replacement of faulty equipment.
4. Survey Results: Suppose a survey is conducted with 280 respondents, and 25 answer "yes" to a particular question. Then, 25/280 (approximately 9%) represents the percentage of respondents who agree with that specific statement. This can be used to gauge public opinion on a specific topic or to understand consumer preferences. The size of the sample (280) is also important to consider when interpreting the results; a larger sample size usually leads to more reliable results.
5. Statistical Sampling: 25 out of 280 could represent a sample drawn from a larger population. Statistical techniques can then be used to estimate the characteristics of the entire population based on this sample. The accuracy of this estimation relies on the randomness of the sampling method and the size of the sample relative to the population size. A larger sample size generally leads to more accurate estimations.
Analyzing the Data: Beyond the Simple Percentage
While the percentage (approximately 9%) provides a quick overview, a more in-depth analysis is crucial for making informed decisions. This could involve:
- Comparing to benchmarks: How does the 9% compare to industry standards, historical data, or target goals? Is it significantly higher or lower than expected?
- Considering other variables: Are there other factors that might influence the ratio? For example, in the marketing email scenario, the day of the week or the time of day the emails were sent could affect the conversion rate.
- Performing statistical tests: If the data comes from a sample, statistical tests can determine if the observed ratio is statistically significant or simply due to random chance. This helps to avoid drawing inaccurate conclusions from limited data.
- Visualizing the data: Graphs and charts (like pie charts or bar graphs) can help to visually represent the data and make it easier to understand and communicate to others.
The Importance of Context and Further Exploration
The interpretation of 25 out of 280 profoundly depends on the context. Without understanding the underlying situation, the number is meaningless. To illustrate this point further, consider these scenarios:
- Scenario A: 25 out of 280 patients treated for a rare disease experienced complete remission. This is excellent news, possibly indicating a highly effective treatment.
- Scenario B: 25 out of 280 manufactured parts failed quality control. This is alarming and indicates significant issues in the production process.
The same numerical ratio yields drastically different conclusions based solely on context.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How can I calculate the percentage from 25 out of 280 more accurately?
A: Use a calculator or spreadsheet software to divide 25 by 280 and multiply by 100. This will give you a more precise percentage than the approximate 9% we used.
Q: What are some other ways to represent this ratio?
A: Besides a percentage and a simplified fraction, you can express this as a decimal (approximately 0.0893) or a ratio (25:280 or 5:56). The best representation depends on the context and your audience.
Q: Is a sample size of 280 large enough for reliable statistical analysis?
A: The adequacy of a sample size depends on the desired level of precision and the variability within the population. While 280 is a reasonably sized sample for some applications, it might be insufficient for others, especially when dealing with a large or highly variable population.
Q: How can I improve my understanding of ratios and proportions?
A: Practice working with different ratios and proportions in various contexts. Use online resources, textbooks, or work through practice problems to enhance your understanding of these fundamental mathematical concepts.
Conclusion: The Power of Contextual Understanding
The seemingly simple ratio of 25 out of 280 holds significant implications across diverse fields. Its meaning is not inherent in the numbers themselves but lies in the context within which it is observed. This emphasizes the critical importance of analyzing data within its context, considering relevant factors, and using appropriate analytical methods to draw accurate and meaningful conclusions. Understanding ratios and proportions is a fundamental skill applicable across numerous disciplines, and the ability to interpret them effectively is essential for sound decision-making. By focusing on the context, employing appropriate analytical techniques, and considering additional variables, we can transform a simple numerical ratio into a powerful tool for understanding and interpreting complex data.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
10 Oz Ribeye
Sep 10, 2025
-
96f To C
Sep 10, 2025
-
10 Of 12 00
Sep 10, 2025
-
80kilos In Stone
Sep 10, 2025
-
60ml In Tablespoons
Sep 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 25 Of 280 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.