0.25 Mg Mcg
stanleys
Sep 10, 2025 · 6 min read
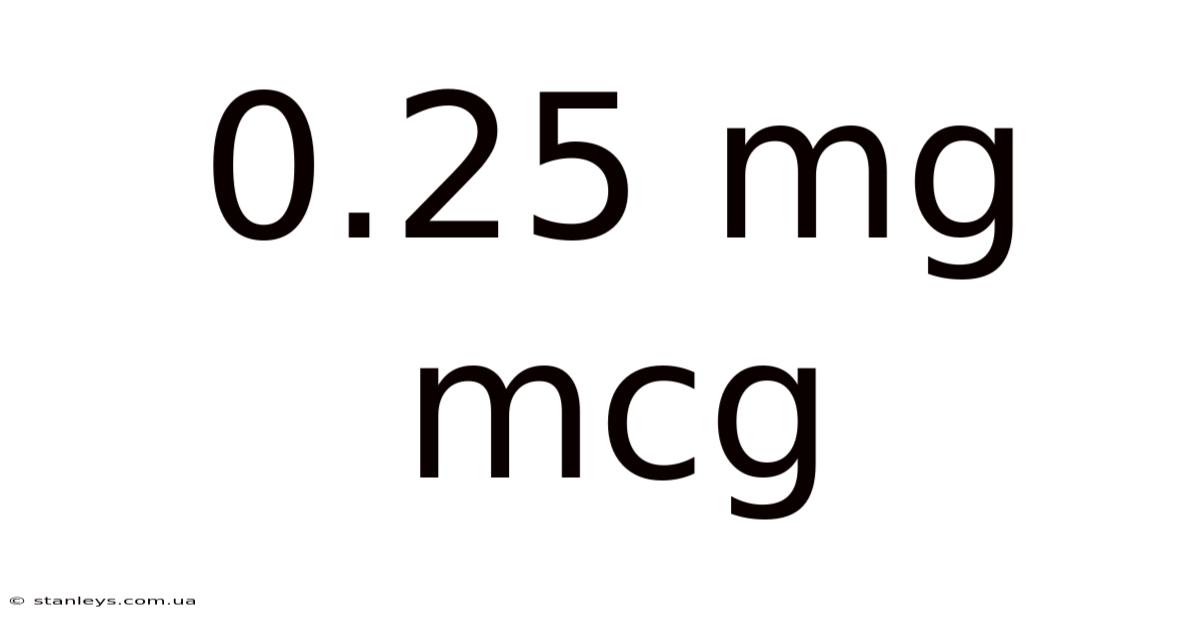
Table of Contents
Decoding the Miniscule: Understanding 0.25 mg vs. mcg
The world of medicine and health often deals with incredibly small measurements. Understanding these units, especially when they're used interchangeably or incorrectly, is crucial for both patients and healthcare professionals. This article will delve deep into the often-confusing comparison between 0.25 mg and mcg, clarifying the difference, explaining their significance in various contexts, and dispelling common misconceptions. This is particularly important when dealing with prescription medications, where even tiny discrepancies can have significant health consequences.
Understanding Milligrams (mg) and Micrograms (mcg)
Before we dive into the comparison, let's establish a clear understanding of the units themselves. Both milligrams (mg) and micrograms (mcg) are units of mass in the metric system, used extensively in measuring dosages of medications and other substances. The key difference lies in their scale:
-
Milligram (mg): One milligram is equal to one-thousandth of a gram (1 mg = 0.001 g). This is a relatively common unit used for measuring many medications and supplements.
-
Microgram (mcg): Also known as a microgram, one microgram is one-millionth of a gram (1 mcg = 0.000001 g). This unit is used for measuring extremely small quantities, often encountered in potent medications or trace elements in nutritional supplements.
The crucial relationship between the two is that 1 mg = 1000 mcg. This conversion factor is vital for accurately interpreting medication dosages and avoiding potential errors.
0.25 mg vs. 0.25 mcg: A World of Difference
The difference between 0.25 mg and 0.25 mcg is substantial, representing a 1000-fold difference. To illustrate this clearly:
-
0.25 mg is equivalent to 250 mcg. This is a relatively common dosage for certain medications.
-
0.25 mcg is a significantly smaller amount, representing only a quarter of a microgram. This dosage is much more likely to be found in medications with extremely high potency or in specialized medical contexts.
Confusing these two values can have serious consequences. Mistaking 0.25 mg for 0.25 mcg could result in a significantly under-dosed medication, rendering it ineffective. Conversely, mistaking 0.25 mcg for 0.25 mg could lead to a massive overdose, potentially causing severe adverse effects or even death.
Real-World Examples and Significance
The significance of accurately understanding the difference between mg and mcg becomes apparent when considering real-world examples. Here are a few scenarios where this distinction is critical:
-
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Many HRT medications, particularly those containing thyroid hormones or estrogen, are prescribed in microgram dosages. A misinterpretation of the dosage could have a significant impact on hormone levels and overall health. Accurate understanding of mcg values is paramount.
-
Vitamin and Mineral Supplements: Some vitamins and minerals, especially those present in trace amounts, are measured in micrograms. While often considered less critical than medication dosages, accurately measuring micronutrients is still essential for optimal health.
-
Cardiovascular Medications: Certain medications used to treat cardiovascular conditions might have dosages prescribed in both mg and mcg, depending on the specific drug and the patient's needs. Accurate conversion and understanding are critical to ensure appropriate dosing.
Common Misconceptions and Errors
A common source of confusion stems from the similar appearance of "mg" and "mcg," particularly in handwritten prescriptions or less clear digital formats. This can lead to several potential errors:
-
Misreading Prescriptions: A simple error in reading or interpreting a prescription can have devastating consequences. Always double-check the dosage units to ensure accuracy.
-
Incorrect Conversions: Mistakes in converting between mg and mcg are frequent. Using an incorrect conversion factor can lead to dangerous overdoses or ineffective treatment.
-
Ambiguous Labeling: Some medications or supplements might not clearly distinguish between mg and mcg on their labels, leading to confusion and potential errors. Always carefully review the product information for clear dosage instructions.
Steps to Avoid Errors in Medication Dosage
Several steps can be taken to minimize the risk of errors related to mg and mcg:
-
Always Double-Check: Carefully examine the prescription and medication labels, paying close attention to both the numerical value and the unit of measurement (mg or mcg).
-
Use Conversion Factors: If you need to convert between mg and mcg, always use the correct conversion factor (1 mg = 1000 mcg).
-
Consult a Pharmacist: If you have any questions or uncertainties about medication dosages, consult your pharmacist. They are trained to interpret prescriptions and provide clarification on dosage units.
-
Keep Records: Maintain a clear and organized record of your medications, including their dosages and units of measurement.
-
Ask Questions: Don’t hesitate to ask your doctor or pharmacist any questions you may have about your medication, including the meaning and significance of the dosage units.
The Scientific Explanation of the Metric System's Prefixes
The metric system is based on powers of ten, making conversions relatively straightforward. Understanding the prefixes used in the metric system is crucial:
-
Milli- (m): Represents 10⁻³ (one-thousandth). Therefore, 1 milligram (mg) is 10⁻³ grams.
-
Micro- (µ): Represents 10⁻⁶ (one-millionth). Therefore, 1 microgram (mcg) is 10⁻⁶ grams.
This systematic approach allows for easy conversion between units. Remembering these prefixes and their numerical values is essential for accurately interpreting measurements in various scientific and medical contexts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can I take 0.25 mg instead of 0.25 mcg?
A: Absolutely not. 0.25 mg is 1000 times larger than 0.25 mcg. Taking 0.25 mg when 0.25 mcg is prescribed could result in a serious overdose.
Q: How can I easily convert between mg and mcg?
A: To convert from mg to mcg, multiply by 1000. To convert from mcg to mg, divide by 1000.
Q: Why are both mg and mcg used in medicine?
A: The choice between mg and mcg depends on the potency of the medication. Potent medications, requiring extremely small doses, are often measured in mcg, while less potent medications are measured in mg.
Q: What should I do if I suspect a dosage error on my prescription?
A: Immediately contact your doctor or pharmacist to clarify the dosage. Do not take the medication until you have confirmed the correct dosage.
Conclusion: Precision is Paramount
Understanding the difference between 0.25 mg and 0.25 mcg is not merely an academic exercise; it's a matter of patient safety and treatment efficacy. The 1000-fold difference between these units highlights the critical importance of precise measurement and careful interpretation of medication dosages. By understanding the metric system, its prefixes, and the potential consequences of misinterpreting these units, both patients and healthcare professionals can work together to ensure safe and effective medical treatment. Always double-check, ask questions, and never hesitate to seek clarification when in doubt. Your health depends on it.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Half Of 135
Sep 10, 2025
-
275mm To Cm
Sep 10, 2025
-
99kg In Stones
Sep 10, 2025
-
85g To Ounces
Sep 10, 2025
-
40 Of 160
Sep 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 0.25 Mg Mcg . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.