X 4 81
stanleys
Sep 21, 2025 · 6 min read
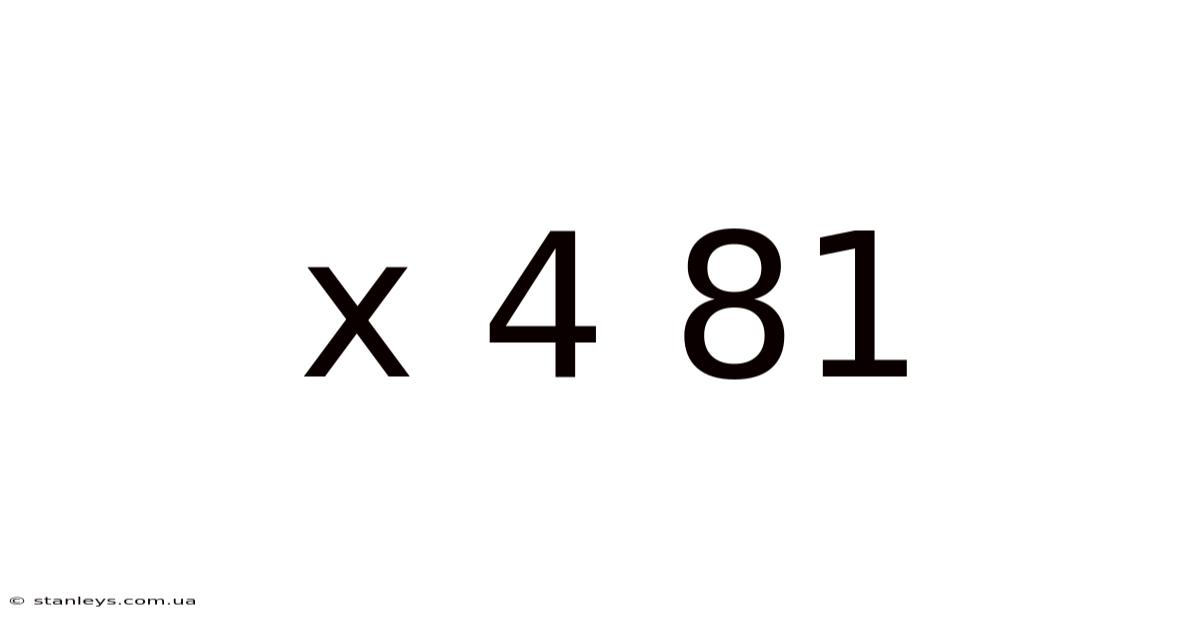
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery: Exploring the Mathematical Significance of x⁴ + 81
The expression x⁴ + 81 might seem simple at first glance, a straightforward polynomial. However, a deeper dive reveals a surprisingly rich mathematical landscape, involving complex numbers, factorization techniques, and elegant algebraic manipulations. This exploration will delve into the intricacies of this expression, unraveling its secrets and showcasing its significance in various mathematical contexts. We'll examine its factorization, its roots, and its applications, ultimately demonstrating that seemingly simple expressions often hide profound mathematical depth.
Understanding the Challenge: Why Factoring x⁴ + 81 Isn't Straightforward
Unlike simpler quadratic expressions, x⁴ + 81 doesn't readily factor using standard methods. We can't simply apply the difference of squares formula (a² - b²) = (a + b)(a - b) because we have a sum of two terms, not a difference. The sum of squares (a² + b²) is only factorable using complex numbers. This immediately hints at the involvement of complex numbers in the factorization of x⁴ + 81.
The Power of Complex Numbers: Unlocking the Factorization
The key to factoring x⁴ + 81 lies in recognizing it as a sum of squares, but not in the real number system. We need to extend our number system to include complex numbers. Recall that the imaginary unit i is defined as √(-1). Using this, we can rewrite x⁴ + 81 as a difference of squares in the complex domain:
x⁴ + 81 = (x²)² - (9i²) = (x² - 9i)(x² + 9i)
This is a crucial step. We've cleverly transformed the sum of squares into a difference of squares using the properties of complex numbers. However, we can factor this further. Let's focus on the first term:
x² - 9i = x² - (3√i)²
To proceed, we must express 9i in polar form. Recall that a complex number z = a + bi can be represented in polar form as z = r(cosθ + isinθ), where r = √(a² + b²) and θ = arctan(b/a). For 9i, r = 9 and θ = π/2. Therefore:
9i = 9(cos(π/2) + isin(π/2))
Using Euler's formula, e^(iθ) = cosθ + isinθ, we can simplify this further:
9i = 9e^(iπ/2)
This allows us to find the square root of 9i more easily:
√(9i) = √9 * √(e^(iπ/2)) = 3e^(iπ/4) and 3e^(i5π/4)
Therefore, using the polar form, we find the square root of 9i is approximately 3(cos(π/4) + isin(π/4)) = 3(1/√2 + i/√2) = (3√2)/2 + i(3√2)/2 and 3(cos(5π/4) + isin(5π/4)) = -(3√2)/2 - i(3√2)/2.
Similarly, we can factor the second term, x² + 9i. This process involves similar steps, resulting in two additional factors involving complex numbers. The complete factorization will then involve four linear factors, each containing a complex root.
Finding the Roots: Delving into the Complex Plane
The factorization reveals the four roots of the equation x⁴ + 81 = 0. These roots are complex numbers and are symmetrically distributed in the complex plane. Understanding the distribution of roots provides valuable insight into the behavior of the polynomial.
Let's denote the roots as r₁, r₂, r₃, and r₄. These roots are non-real complex numbers and can be expressed using polar coordinates or rectangular coordinates. They are evenly spaced around a circle in the complex plane with radius 3, which is the fourth root of 81.
By applying De Moivre's theorem, a powerful tool in the realm of complex numbers, we can derive these roots. De Moivre's theorem states that (cos θ + i sin θ)^n = cos nθ + i sin nθ.
This elegant theorem allows for the easy calculation of the four distinct roots of x⁴ = -81. We can express -81 in polar form as 81(cos π + i sin π). Applying De Moivre's theorem, we find the four roots.
The four roots are:
- r₁ = 3(cos(π/4) + i sin(π/4))
- r₂ = 3(cos(3π/4) + i sin(3π/4))
- r₃ = 3(cos(5π/4) + i sin(5π/4))
- r₄ = 3(cos(7π/4) + i sin(7π/4))
These roots represent points in the complex plane, demonstrating the interconnectedness of algebra and geometry in complex analysis.
Applications and Significance: Beyond the Theoretical
While the factorization and roots might seem purely theoretical, they have applications in various fields. Understanding complex roots is crucial in:
- Signal Processing: Complex numbers are fundamental to representing and manipulating signals in various domains, and understanding polynomial roots aids in analyzing signal behavior.
- Control Systems: Control systems engineering often deals with characteristic equations that involve polynomials, and the roots of these polynomials determine the stability and performance of the systems.
- Quantum Mechanics: Complex numbers play a vital role in quantum mechanics, and understanding the roots of polynomials is essential for solving various quantum mechanical problems.
- Advanced Algebra and Number Theory: The study of such expressions contributes to a deeper understanding of abstract algebraic structures and number theory concepts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can x⁴ + 81 be factored using only real numbers?
A1: No. The sum of two even powers, such as x⁴ + 81, cannot be factored using only real numbers. The introduction of complex numbers is necessary for complete factorization.
Q2: What is the significance of the roots being complex?
A2: The complex roots indicate the polynomial has no real roots. This means the graph of y = x⁴ + 81 never intersects the x-axis. The complex roots highlight the limitations of working solely within the real number system.
Q3: How can I verify the factorization?
A3: Multiplying the four factors obtained from the factorization process will yield the original expression, x⁴ + 81, confirming the correctness of the factorization. This can be a tedious but valuable exercise in confirming the validity of the complex number manipulation.
Q4: Are there other ways to approach this factorization problem?
A4: While the method presented here is efficient and elegant, there exist alternative approaches. One such approach is the use of the resolvent cubic equation, a more general technique for solving higher-order polynomial equations. This technique however will still lead to the same complex roots.
Conclusion: A Journey into the Heart of Mathematics
The seemingly simple expression x⁴ + 81 unveils a surprisingly rich mathematical tapestry. Its factorization, the nature of its complex roots, and its applications across various fields demonstrate the power and elegance of complex numbers and the beauty of mathematical exploration. This exploration highlights the interconnectedness of different mathematical concepts and emphasizes that even seemingly simple expressions can lead to profound insights and applications within the broader mathematical landscape. The journey through this problem exemplifies the spirit of mathematical inquiry—the pursuit of understanding beyond the immediately apparent.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 4 81 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.