8 Of 300
stanleys
Sep 14, 2025 · 7 min read
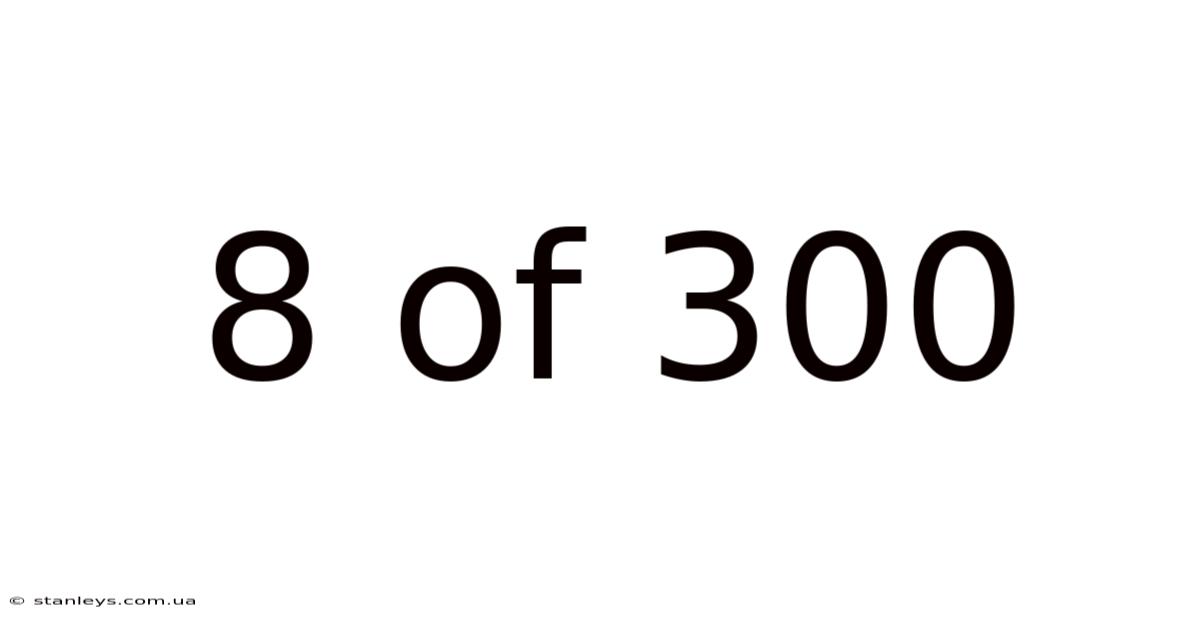
Table of Contents
Decoding the Enigma: Understanding the Significance of "8 of 300"
The phrase "8 of 300" might seem cryptic at first glance. It's not a well-known idiom or a common expression. However, within specific contexts, particularly those relating to statistical analysis, probability, and decision-making, this phrase represents a powerful concept with far-reaching implications. This article will delve into the meaning and significance of "8 of 300," exploring its applications in various fields and highlighting its relevance in understanding data and making informed choices. We will unpack its core meaning, explore its practical applications, and discuss its limitations. We’ll also address common questions and misconceptions surrounding this seemingly simple phrase.
Understanding the Core Concept: Proportion and Significance
At its heart, "8 of 300" represents a proportion or a ratio. It signifies that out of a total of 300 observations, events, or data points, 8 possess a specific characteristic, quality, or outcome. This simple ratio (8/300) can be expressed as a percentage (approximately 2.67%) or a decimal (0.0267). While seemingly insignificant at first, the true meaning depends heavily on the context. The significance lies not just in the raw numbers but in their implications within the larger picture.
For example, if we are talking about the success rate of a new drug trial, "8 of 300" might indicate a very low success rate, raising concerns about the drug's efficacy. On the other hand, if we're discussing the occurrence of a rare genetic mutation in a population sample, "8 of 300" might represent a surprisingly high prevalence, warranting further investigation.
Applications in Different Fields: From Medicine to Marketing
The principle of "8 of 300" finds applications across a wide range of disciplines:
1. Medical Research and Clinical Trials: In clinical trials, the number of patients experiencing a positive outcome (e.g., remission of a disease) compared to the total number of participants is crucial. "8 of 300" in this context would indicate a relatively low success rate, prompting further analysis of the treatment's efficacy, potential side effects, and the need for improved methodologies. This data is vital for determining whether a treatment is worth pursuing further or requires modifications.
2. Quality Control and Manufacturing: In manufacturing, "8 of 300" could represent the number of defective products found in a batch. This information is vital for assessing the quality control processes and identifying potential sources of defects to improve manufacturing efficiency and reduce waste. A higher number would signify a serious quality control issue demanding immediate attention.
3. Market Research and Sales: In marketing, "8 of 300" might represent the number of customers who responded positively to a new advertising campaign out of a sample of 300. This allows marketers to assess the campaign's effectiveness and make data-driven decisions regarding future marketing strategies. A low response rate might suggest the need to revise the campaign's messaging or target audience.
4. Environmental Science and Ecology: In ecological studies, "8 of 300" might refer to the number of a specific species observed in a sample area. This provides crucial data for assessing population size, distribution, and conservation status. A low number could indicate a declining population, requiring conservation efforts.
5. Social Sciences and Surveys: Researchers in social sciences use surveys to collect data on various aspects of human behavior and attitudes. "8 of 300" in a survey context could represent the number of respondents who answered a particular question in a certain way. This allows researchers to analyze trends, preferences, and opinions within the surveyed population.
The Significance of Statistical Significance Testing
Simply stating that "8 of 300" shows a certain proportion is not enough. The real power of interpreting this data lies in statistical significance testing. This involves determining whether the observed proportion (8 out of 300) is statistically different from what would be expected by chance. Several statistical tests can be used, such as the chi-squared test or a z-test for proportions. These tests help us determine if the observed result is likely due to a real effect or just random variation.
The concept of p-value is crucial here. The p-value represents the probability of observing the obtained results (or more extreme results) if there were actually no real effect. A low p-value (typically below 0.05) indicates that the observed proportion is statistically significant, meaning it's unlikely to have occurred by chance alone. In other words, a low p-value suggests there’s a real difference or effect. However, the p-value should always be interpreted in conjunction with the effect size (the magnitude of the difference) and the context of the study.
Limitations and Misinterpretations
It's crucial to acknowledge the limitations of interpreting "8 of 300" without sufficient context and statistical analysis.
- Sample Size: A sample size of 300 might be considered relatively small in some contexts, potentially leading to unreliable conclusions. Larger sample sizes generally provide more robust and reliable results.
- Sampling Bias: The way the sample of 300 was selected is crucial. If the sample is biased (not representative of the population of interest), then the conclusions drawn from "8 of 300" might be inaccurate and misleading.
- Confounding Variables: Other factors not considered in the analysis might be influencing the outcome. Failing to account for confounding variables can lead to incorrect interpretations of the data.
- Oversimplification: Reducing complex phenomena to a simple ratio like "8 of 300" can be an oversimplification. It's essential to consider the broader context and other relevant data points.
Expanding the Understanding: Beyond the Numbers
The interpretation of "8 of 300" necessitates a deeper understanding beyond the raw numbers. Several factors contribute to a complete and accurate interpretation:
- The nature of the 300: What exactly are these 300 entities? Are they patients in a clinical trial, products in a manufacturing line, responses to a survey, or something else?
- The nature of the 8: What characterizes these 8 entities? Are they successful treatments, defective products, positive responses, or something else?
- The context: What is the broader context of the study or experiment? What questions are being addressed? What are the implications of the findings?
- Statistical analysis: What statistical tests have been performed to assess the significance of the observed proportion? What is the p-value, and what does it mean in the context of the study?
By carefully considering these factors, a more nuanced and accurate interpretation of "8 of 300" can be achieved.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Is "8 of 300" a statistically significant result?
A: Whether "8 of 300" is statistically significant depends entirely on the context and the statistical tests performed. Without further information about the study and the appropriate statistical analysis, it's impossible to determine statistical significance.
Q: How can I determine the statistical significance of "8 of 300"?
A: To determine statistical significance, you need to perform a statistical test, such as a chi-squared test or a z-test for proportions, taking into account the expected proportion under the null hypothesis (e.g., no effect). Statistical software packages can easily perform these calculations.
Q: What if the sample size were larger, say 3000, and the number of successes remained 80 (8% instead of 2.67%)?
A: While the proportion remains the same, a larger sample size (3000) would provide more statistical power. This means a smaller difference from the expected proportion could be deemed statistically significant with a larger sample size.
Q: Can "8 of 300" be used to predict future outcomes?
A: While "8 of 300" provides information about past events, it can be used to estimate future outcomes. However, such estimations should be made cautiously and should take into account the limitations discussed earlier, such as potential sampling bias and confounding variables.
Conclusion: The Power of Context and Critical Analysis
The phrase "8 of 300" is more than just a simple ratio; it's a starting point for critical analysis and data-driven decision-making. Its significance hinges entirely on the context in which it's presented. Without a thorough understanding of the underlying data, the associated experimental design, and the appropriate statistical analysis, drawing meaningful conclusions from such a proportion would be premature and potentially misleading. The true power of understanding "8 of 300" lies in recognizing the importance of statistical significance testing, considering potential biases, and interpreting the results within their broader context. Only then can we truly unlock the valuable insights hidden within this seemingly simple phrase.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
76kgs In Stone
Sep 14, 2025
-
5 3 As Decimal
Sep 14, 2025
-
Books Of Synonyms
Sep 14, 2025
-
45 Of 30
Sep 14, 2025
-
3400 X 12
Sep 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 8 Of 300 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.