75 Of 20
stanleys
Sep 16, 2025 · 7 min read
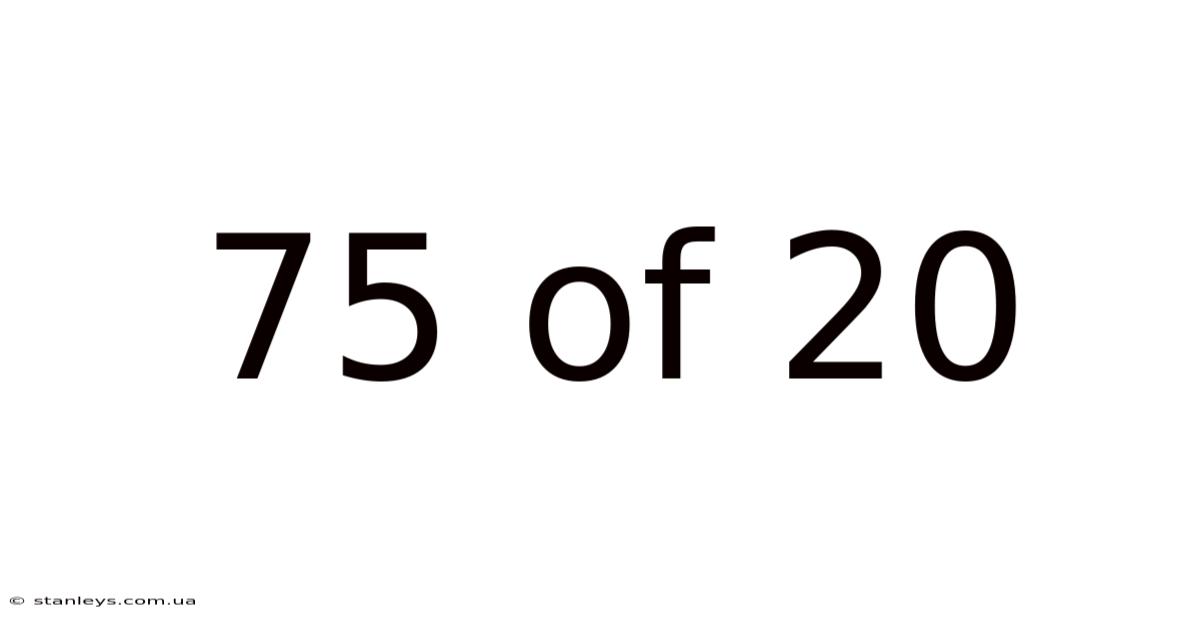
Table of Contents
Decoding the Enigma: Understanding 75 out of 20 in Different Contexts
The phrase "75 out of 20" immediately strikes us as illogical. We're accustomed to percentages and ratios where the numerator (the top number) is less than or equal to the denominator (the bottom number). So, what does "75 out of 20" really mean? This seemingly nonsensical expression can actually represent several different scenarios, depending on the context. This article will explore these possibilities, delving into the mathematical interpretations, potential real-world applications, and the importance of understanding the underlying principles behind such expressions.
1. Introduction: Beyond the Obvious
At first glance, "75 out of 20" seems mathematically impossible. In a standard fractional representation (75/20), we have a top-heavy fraction, also known as an improper fraction. This isn't inherently wrong; it simply indicates a value greater than one. However, the phrasing itself suggests a count or a score, which is where the ambiguity lies. Are we dealing with a simple mathematical expression, a misunderstanding of terminology, or something more nuanced? Let's examine the potential interpretations.
2. Mathematical Interpretations: Fractions, Percentages, and Ratios
A. Improper Fraction and Mixed Number: The most straightforward interpretation is as an improper fraction. 75/20 simplifies to 15/4, which can be expressed as a mixed number: 3 ¾. This means the value represents three and three-quarters of a whole unit.
B. Percentage Calculation: To express this as a percentage, we divide the numerator by the denominator and multiply by 100: (75/20) * 100 = 375%. This signifies that the value exceeds the baseline by 275%. This is a common way to represent exceeding a target or quota. For example, if a sales target was 20 units and 75 units were sold, the sales exceeded the target by 375%.
C. Ratio Representation: "75 out of 20" can also be considered a ratio, expressing a relationship between two quantities. It's important to understand that ratios don't necessarily represent parts of a whole. This ratio (75:20) simplifies to 15:4, illustrating the proportional relationship between the two quantities. Think of it like this: for every 4 units of one thing, there are 15 units of another.
3. Real-World Applications: Unpacking the Scenarios
The interpretation of "75 out of 20" depends heavily on its context. Here are several potential scenarios:
A. Exceeding Expectations/Targets: This is the most likely scenario. Imagine a sales team with a monthly target of 20 sales. If they achieve 75 sales, they've significantly surpassed their goal. The phrase "75 out of 20" would accurately describe their performance, emphasizing the substantial overachievement. This context makes the improper fraction perfectly reasonable.
B. Aggregate Data from Multiple Sources: Imagine data collected from multiple sources or over multiple periods. Perhaps there are 20 data points from one source and 55 from another. If you combine those, you'd get a total of 75 data points from 20 initial sources. This could be used when describing an aggregation process rather than a proportion. The "20" represents the original number of data points collected, while "75" represents the total number collected across all sources.
C. Misunderstanding or Miscommunication: It's also possible that "75 out of 20" represents a simple misunderstanding or error in recording data. Perhaps the numbers were accidentally transposed, or there was a mistake in counting or calculation. In such cases, clarifying the correct figures would be crucial.
D. Multiple Rounds or Iterations: Consider a game or a process with multiple rounds. If a certain objective needs to be achieved 20 times, and it's achieved 75 times, then this could represent the number of successes against a smaller set of required instances. The ratio highlights the efficiency or effectiveness exceeding the original expectation.
E. Statistical Anomalies or Outliers: In statistical analysis, "75 out of 20" could signify an anomalous dataset, where a surprisingly high number of instances (75) emerges from a smaller sample size (20). This could require further investigation to understand the underlying causes of this significant deviation.
4. Mathematical Explanation and Further Exploration
Understanding the underlying mathematics is key to interpreting "75 out of 20." Let's revisit the concepts:
- Fractions: A fraction (a/b) represents a part of a whole, where 'a' is the numerator and 'b' is the denominator. In "75 out of 20," 75 is the part and 20 is the whole (or the reference point).
- Improper Fractions: When the numerator (a) is greater than the denominator (b), the fraction is called an improper fraction. This indicates a value greater than one.
- Mixed Numbers: Improper fractions can be converted into mixed numbers (a + b/c), which represent a whole number plus a fraction. This offers a more intuitive representation of the value.
- Percentages: Percentages express fractions as a proportion of 100. Converting "75 out of 20" to a percentage highlights the magnitude of the value exceeding the baseline.
- Ratios: Ratios (a:b) compare two quantities. The ratio "75:20" simplifies to 15:4, indicating a proportional relationship between two values.
It's important to note that the context is crucial in determining the correct mathematical interpretation. The same numerical expression can represent different situations depending on what is being measured and how it's being reported.
5. Illustrative Examples
Let's consider some concrete examples to solidify our understanding:
Example 1: Sales Target: A sales team aims to sell 20 units in a month. They manage to sell 75 units. Their performance is "75 out of 20," indicating a 375% achievement rate, showing a substantial over-performance.
Example 2: Survey Responses: A survey is sent to 20 participants. A total of 75 responses are received (perhaps some participants gave multiple responses). The number of responses is reported as "75 out of 20," illustrating that the response rate greatly exceeded the initial participant count.
Example 3: Data Aggregation: 20 different sensors collect data. Combining all the data points, a total of 75 data points are aggregated from the 20 sensors. The phrase "75 out of 20" represents the aggregated data points relative to the original number of data sources.
6. FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is "75 out of 20" mathematically correct?
A: Mathematically, it's not incorrect, but it's unusual. As an improper fraction or a ratio, it's perfectly valid. The issue lies in the typical interpretation of "out of," which often implies a part of a whole, where the numerator is less than the denominator.
Q: How can I avoid misinterpretations of such expressions?
A: Always check the context. Consider what the numbers represent. If possible, ask for clarification if the expression seems ambiguous or illogical. Using clear and unambiguous language when presenting data is essential to avoid misunderstandings.
Q: What is the best way to represent "75 out of 20"?
A: The best representation depends on the context. A percentage (375%) would be suitable for showing overachievement. A ratio (15:4) would show the proportionality between the two numbers. A clear textual explanation would always add to clarity.
7. Conclusion: Context is King
The phrase "75 out of 20" is not inherently wrong but requires careful contextual interpretation. Depending on the situation, it can represent exceeding targets, aggregated data from multiple sources, a statistical anomaly, or even a simple error. Understanding the mathematical principles behind fractions, percentages, and ratios allows us to decode the meaning correctly. The key takeaway is that while the numerical expression is unusual, the underlying mathematical concepts remain valid. Always prioritize clarity in communication, and ensure that the context makes the meaning evident to avoid ambiguity and misunderstanding. The ability to interpret such unusual expressions is a valuable skill in various fields, from data analysis and business reporting to interpreting research findings and solving real-world problems. Remember to always look beyond the surface and delve into the context before drawing conclusions.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 75 Of 20 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.