60 Of 220
stanleys
Sep 21, 2025 · 6 min read
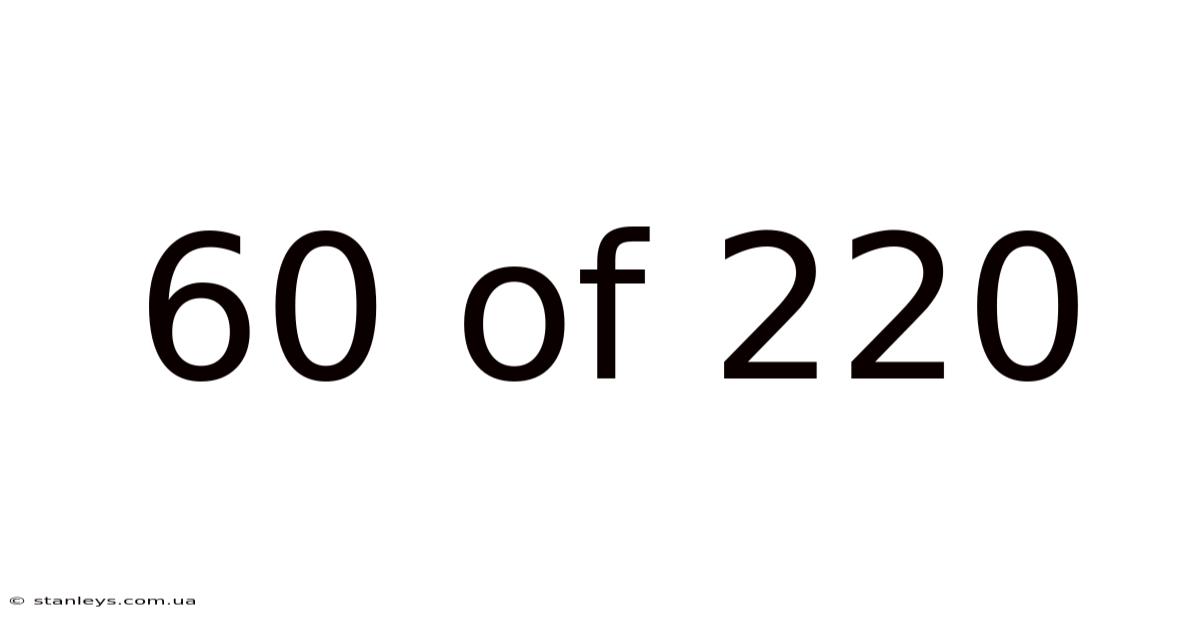
Table of Contents
Understanding the Fraction 60/220: Simplification, Decimals, and Real-World Applications
The fraction 60/220, at first glance, might seem intimidating. However, understanding this fraction involves fundamental concepts in mathematics, applicable not only in academic settings but also in everyday life. This article will provide a comprehensive exploration of 60/220, covering its simplification, decimal equivalent, percentage representation, and various real-world examples to solidify your understanding. We'll delve into the methods for simplifying fractions, explore the relationship between fractions, decimals, and percentages, and illustrate how these concepts are applied practically.
I. Simplifying the Fraction 60/220
The first step in understanding 60/220 is to simplify it to its lowest terms. This means finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numerator (60) and the denominator (220) and dividing both by it. The GCD is the largest number that divides both 60 and 220 without leaving a remainder.
One method to find the GCD is by listing the factors of both numbers:
- Factors of 60: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 10, 12, 15, 20, 30, 60
- Factors of 220: 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, 11, 20, 22, 44, 55, 110, 220
The largest common factor is 20.
Therefore, we divide both the numerator and the denominator by 20:
60 ÷ 20 = 3
220 ÷ 20 = 11
This simplifies 60/220 to 3/11. This simplified fraction is equivalent to the original fraction but is easier to work with. Using the prime factorization method offers another, often more efficient way to find the GCD. Let's break down both 60 and 220 into their prime factors:
- 60 = 2 x 2 x 3 x 5 = 2² x 3 x 5
- 220 = 2 x 2 x 5 x 11 = 2² x 5 x 11
The common prime factors are 2² and 5. Multiplying these together (2 x 2 x 5 = 20) gives us the GCD, confirming our previous result.
II. Converting 60/220 (or 3/11) to a Decimal
Converting a fraction to a decimal involves dividing the numerator by the denominator. In this case, we'll use the simplified fraction 3/11:
3 ÷ 11 = 0.272727...
Notice the repeating pattern "27". This indicates a recurring decimal. We can represent this using a bar over the repeating digits: 0.27̅
Therefore, the decimal equivalent of 60/220 is approximately 0.27. The approximation is necessary because the decimal representation is infinite. Depending on the context, you might round to a specific number of decimal places (e.g., 0.273 if rounding to three decimal places).
III. Expressing 60/220 as a Percentage
To express a fraction as a percentage, multiply the decimal equivalent by 100. Using the decimal equivalent of 3/11 (0.2727...):
0.2727... x 100 = 27.2727...%
This can be rounded to 27.27% or even 27% depending on the required precision.
IV. Real-World Applications of 60/220 (and Equivalent Fractions)
The fraction 60/220, or its simplified form 3/11, can represent various scenarios in real life. Understanding how to apply these concepts is crucial for practical problem-solving. Here are some examples:
-
Proportions: Imagine you have a bag of 220 marbles, 60 of which are red. The fraction 60/220 (or 3/11) represents the proportion of red marbles in the bag. This proportion can be used to predict the number of red marbles in a smaller or larger sample from the same bag.
-
Discounts: A store offers a 60/220 discount on an item. This means a reduction of 60 units for every 220 units purchased, equivalent to a 27.27% discount.
-
Surveys and Statistics: If 60 out of 220 respondents in a survey answered "yes" to a particular question, the fraction 3/11 reflects the proportion of "yes" answers. This proportion is vital in analyzing survey data and drawing conclusions.
-
Recipe Scaling: A recipe calls for 60 grams of flour for 220 grams of dough. You can use the fraction 3/11 to scale the recipe up or down, maintaining the same proportions. For example, if you want to make only 110 grams of dough, you'd need 15 grams of flour (110 x 3/11).
-
Probability: If there are 220 equally likely outcomes in an event, and 60 of those outcomes result in a specific event, then the probability of that specific event is 60/220 or 3/11 (approximately 27.27%).
V. Understanding Fractions, Decimals, and Percentages
It’s essential to understand the interconnectedness of fractions, decimals, and percentages. They all represent parts of a whole, but in different formats:
-
Fraction: Represents a part of a whole as a ratio of two integers (numerator/denominator).
-
Decimal: Represents a part of a whole using base-10 notation (e.g., 0.27).
-
Percentage: Represents a part of a whole as a fraction of 100 (e.g., 27.27%).
The ability to convert between these formats is crucial for solving problems involving proportions, ratios, and percentages. This ability makes you more flexible and efficient in approaching numerical problems.
VI. Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
While we have focused on the basic understanding and applications of 60/220, further exploration can delve into more advanced mathematical concepts:
-
Rational Numbers: Fractions like 60/220 belong to the set of rational numbers – numbers that can be expressed as a ratio of two integers. Understanding rational numbers provides a broader mathematical framework for working with fractions.
-
Irrational Numbers: While 3/11 has a recurring decimal representation, not all fractions produce recurring decimals. Some fractions result in non-repeating, non-terminating decimals (irrational numbers). This highlights the difference and relationship between rational and irrational numbers.
-
Continued Fractions: A fraction can be represented as a continued fraction, an expression of nested fractions. This is an advanced concept often used in number theory and other mathematical fields.
-
Algebraic Applications: Fractions are fundamentally important in algebra, particularly in solving equations and working with algebraic expressions.
VII. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the simplest form of 60/220?
A: The simplest form of 60/220 is 3/11.
Q: Is 60/220 a proper or improper fraction?
A: 60/220 is a proper fraction because the numerator (60) is smaller than the denominator (220).
Q: How do I convert 3/11 to a percentage?
A: Divide 3 by 11 (0.2727...), then multiply by 100 to get approximately 27.27%.
Q: Are there other ways to simplify fractions besides finding the GCD?
A: Yes, you can simplify a fraction by repeatedly dividing both the numerator and denominator by common factors until no common factors remain. The GCD method is just a more efficient way to achieve the same result.
Q: What if I need to round the decimal representation of 3/11?
A: Rounding depends on the context. Rounding to two decimal places would give 0.27, while rounding to three decimal places would give 0.273.
VIII. Conclusion
Understanding the fraction 60/220, its simplification to 3/11, and its decimal and percentage equivalents provides a strong foundation in basic mathematics. The ability to simplify fractions, convert between different representations, and apply these concepts to real-world problems is crucial for success in various fields, from everyday budgeting and cooking to advanced scientific and engineering applications. Remember that mastering these fundamental concepts opens doors to more advanced mathematical explorations. So, practice these techniques and build upon your understanding!
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 60 Of 220 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.