5 Of 250
stanleys
Sep 11, 2025 · 6 min read
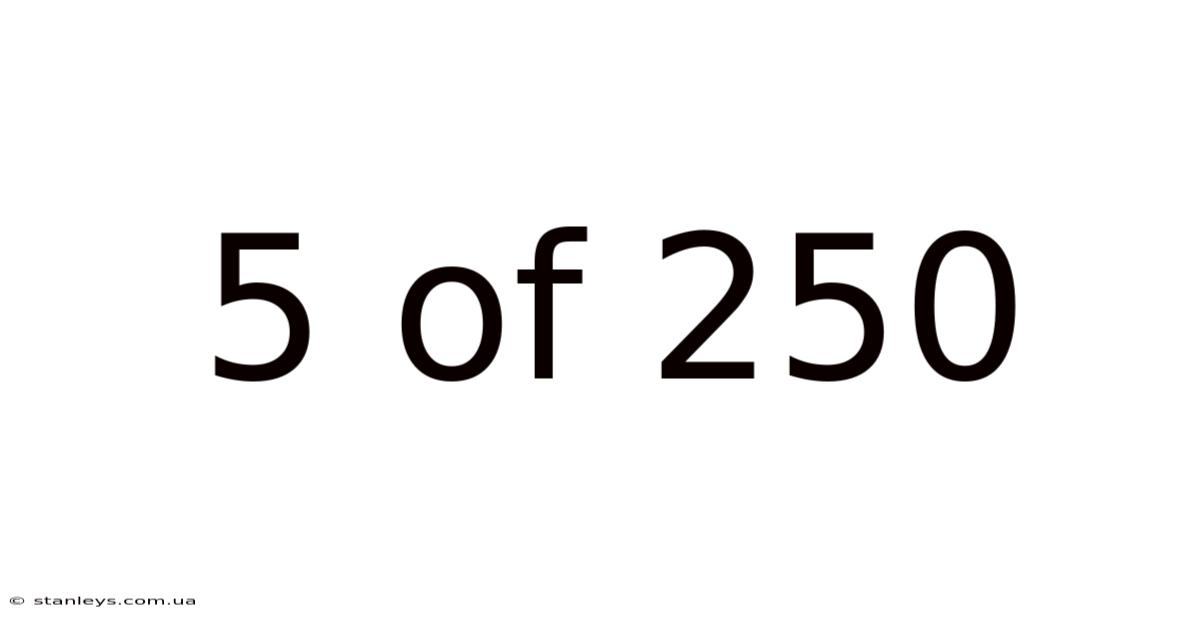
Table of Contents
Decoding the Enigma: Understanding and Mastering the 5 of 250 Ratio in Various Contexts
The seemingly simple ratio of 5 out of 250, or 5/250, often hides a deeper significance depending on the context. This article delves into the meaning and implications of this ratio across different fields, providing a comprehensive understanding accessible to all readers. We'll explore how this seemingly small fraction can represent significant statistical probabilities, crucial engineering tolerances, or even impactful social phenomena. Understanding this ratio helps us interpret data, make informed decisions, and appreciate the nuanced world of proportions.
Understanding the Basics: The 2% Significance
At its core, 5/250 simplifies to 1/50, or 2%. This seemingly small percentage holds considerable weight depending on the context. A 2% failure rate in a manufacturing process might be unacceptable, while a 2% positive response rate to a marketing campaign could be considered a significant success. The absolute number of occurrences (5 in this case) is equally vital; 5 defective parts out of 250 might be manageable, but 500 defective parts out of 25,000 would be a far more serious issue.
Key takeaway: The significance of 5/250 (or 2%) is entirely context-dependent. The scale of the overall sample size, the potential consequences of the ratio, and the specific field of application all contribute to its interpretation.
Applications in Various Fields: From Manufacturing to Medicine
The 5/250 ratio, or its equivalent 2%, finds application in diverse fields:
1. Quality Control and Manufacturing:
In manufacturing, a 2% defect rate is often a benchmark. Imagine a factory producing 250 widgets. Finding 5 defective widgets indicates a 2% defect rate. This might be acceptable depending on industry standards and the cost of correcting the defects. However, a consistent 2% defect rate across large production runs could represent a significant problem, requiring process adjustments to improve efficiency and reduce waste. Statistical Process Control (SPC) techniques are often used to monitor and manage such ratios.
2. Medical Research and Clinical Trials:
In medical research, a 2% occurrence rate could be highly significant. For example, if 5 out of 250 patients participating in a clinical trial experience a specific adverse reaction, this warrants thorough investigation. The observed adverse event rate needs to be compared against the expected rate (considering factors like placebo effects) to determine its clinical significance. Further analysis might be necessary to identify contributing factors and adjust treatment protocols.
3. Social Sciences and Surveys:
In social science research, surveys often deal with large sample sizes. If a survey of 250 individuals reveals 5 respondents exhibiting a specific behavior or opinion, this represents a 2% prevalence. While not necessarily representative of the entire population, it could still highlight a noteworthy trend or minority opinion that needs further exploration. Margin of error and confidence intervals are crucial to interpreting such findings accurately.
4. Environmental Science and Pollution Monitoring:
In environmental studies, a 2% contamination rate in a water sample might indicate a localized pollution problem. The small fraction could be viewed as potentially severe, depending on the nature of the contaminant and its health implications. Further investigation would be essential to identify the source and extent of the contamination.
5. Finance and Investment:
In the financial world, a 2% return on investment (ROI) might be considered modest or even insufficient, while a 2% loss could be alarming depending on the size of the investment. This underscores the importance of understanding the context and the overall magnitude of the numbers involved. Risk assessment and portfolio diversification are essential strategies in managing investment risks.
Beyond the Numbers: The Importance of Context and Interpretation
The 5/250 ratio, while seemingly simple, presents a crucial lesson in the importance of context when interpreting data. The absolute numbers, the overall sample size, and the potential consequences are all critical factors influencing the meaning and significance of this ratio. Blindly applying a 2% threshold without considering the specific field and its inherent nuances can lead to incorrect conclusions and potentially detrimental decisions.
Statistical Significance and Hypothesis Testing
In statistical analysis, determining whether a 5/250 ratio is statistically significant requires hypothesis testing. This involves formulating a null hypothesis (e.g., there is no significant difference between observed and expected rates) and an alternative hypothesis (e.g., there is a significant difference). Statistical tests, such as the chi-square test or z-test, are used to determine the probability of observing the 5/250 ratio (or a more extreme result) if the null hypothesis is true. If the probability is below a predetermined significance level (often 0.05 or 5%), the null hypothesis is rejected, suggesting statistical significance.
Practical Considerations and Decision-Making
When encountering a 5/250 ratio, several factors should guide decision-making:
-
Sample Size: A larger sample size provides greater confidence in the accuracy of the ratio. 5/250 might be less reliable than 50/2500, even though both represent a 2% rate.
-
Consequences of Error: The potential costs or implications of a false positive (assuming a problem exists when it doesn't) or a false negative (missing a real problem) must be evaluated.
-
Cost of Investigation: The expense of further investigation or corrective actions must be weighed against the potential benefits.
-
Industry Standards: Benchmarking against industry standards and best practices is essential to assess the acceptability of the 2% rate.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How can I calculate the percentage represented by 5 out of 250?
A1: Divide 5 by 250 and multiply by 100: (5/250) * 100 = 2%.
Q2: Is a 2% failure rate always considered unacceptable?
A2: No. The acceptability of a 2% failure rate depends heavily on the context, the consequences of failure, and industry standards.
Q3: What statistical tests can be used to analyze a 5/250 ratio?
A3: The chi-square test or z-test are appropriate for analyzing the significance of proportions like 5/250.
Q4: How does sample size influence the interpretation of 5/250?
A4: A larger sample size provides greater confidence in the reliability of the 2% rate.
Q5: What other factors should be considered beyond the numerical ratio?
A5: The potential consequences of error, the cost of investigation, and industry standards should all be taken into account.
Conclusion: Beyond the Numbers, Understanding the Context
The 5/250 ratio, representing a seemingly small 2%, illustrates the crucial role of context in interpreting numerical data. While the ratio itself provides a quantitative measure, its true meaning emerges only when considered within the specific domain of application. Understanding the implications of this ratio necessitates evaluating factors such as sample size, potential consequences, cost-benefit analysis, and relevant industry standards. This holistic approach allows for more accurate interpretation, leading to sounder judgments and informed decisions across various fields. Remember, the numbers tell only part of the story; it's the understanding of the context that unlocks the true meaning.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 5 Of 250 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.