48 X 3
stanleys
Sep 21, 2025 · 5 min read
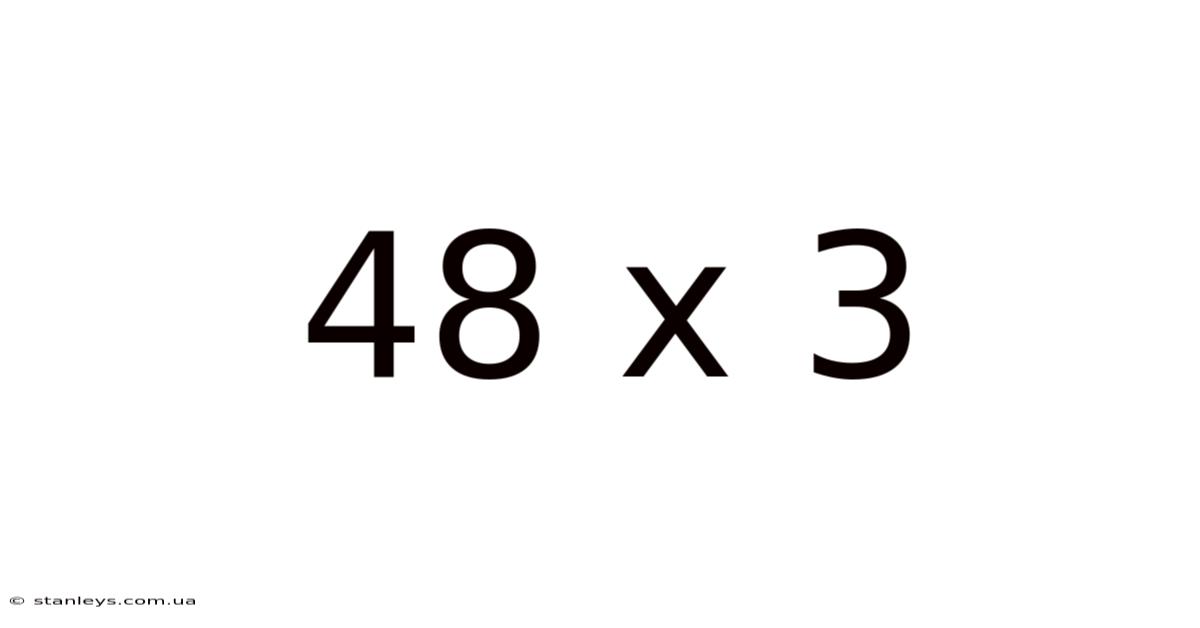
Table of Contents
Decoding 48 x 3: A Deep Dive into Multiplication and Beyond
This article explores the seemingly simple calculation of 48 x 3, unraveling its intricacies and extending the discussion to broader mathematical concepts. We'll delve into various methods for solving this multiplication problem, examining the underlying principles and demonstrating their applicability in more complex scenarios. Whether you're a student brushing up on your multiplication skills, a parent helping your child with homework, or simply curious about the beauty of mathematics, this article offers a comprehensive and engaging exploration of 48 x 3 and its mathematical context.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Multiplication as Repeated Addition
At its core, multiplication is a shortcut for repeated addition. 48 x 3 means adding 48 to itself three times: 48 + 48 + 48. This fundamental understanding is crucial for grasping the essence of multiplication and building a solid mathematical foundation. For smaller numbers, this method is easily visualized and calculated. However, for larger numbers like 48, a more efficient approach is necessary.
Let's break down the repeated addition:
- 48 + 48 = 96
- 96 + 48 = 144
Therefore, 48 x 3 = 144.
Methods for Calculating 48 x 3
While repeated addition works, it's not the most efficient method for larger numbers. Let's explore some alternative approaches:
1. The Standard Algorithm (Column Method)
This is the most commonly taught method in schools. It involves multiplying each digit of 48 by 3, starting with the ones place and then the tens place, carrying over any tens to the next column.
- Step 1: Multiply the ones place: 3 x 8 = 24. Write down 4 and carry-over 2.
- Step 2: Multiply the tens place: 3 x 4 = 12. Add the carry-over 2: 12 + 2 = 14. Write down 14.
- Result: The final answer is 144.
This method systematically breaks down the multiplication into manageable steps, making it easier to handle larger numbers.
2. Distributive Property
The distributive property of multiplication states that a(b + c) = ab + ac. We can use this to break down 48 into smaller, more manageable numbers.
- We can rewrite 48 as 40 + 8.
- Then, 3 x 48 = 3 x (40 + 8) = (3 x 40) + (3 x 8) = 120 + 24 = 144
This method highlights the underlying mathematical principles and offers a more flexible approach to multiplication.
3. Lattice Multiplication
Lattice multiplication is a visual method that can be particularly helpful for understanding the process and for multiplying larger numbers. It's less commonly taught but offers a unique perspective. This method involves creating a grid, performing individual multiplications within the grid, and then summing the diagonals. While detailed explanation requires visual aids, the result remains 144.
Exploring the Concept of Factors and Multiples
The calculation 48 x 3 reveals the relationship between factors and multiples. In this case:
- Factors: 3 and 48 are factors of 144 because they divide 144 without leaving a remainder.
- Multiples: 144 is a multiple of 3 and 48.
Understanding factors and multiples is fundamental to various mathematical concepts, including prime factorization, greatest common divisor (GCD), and least common multiple (LCM).
Applications of Multiplication in Real-World Scenarios
The seemingly simple calculation of 48 x 3 has numerous practical applications:
- Counting Objects: Imagine you have 48 boxes of candies, and each box contains 3 candies. The total number of candies is 48 x 3 = 144.
- Calculating Costs: If an item costs $48, and you buy 3 of them, the total cost is 48 x 3 = $144.
- Measuring Dimensions: If a rectangle has a length of 48 units and a width of 3 units, its area is 48 x 3 = 144 square units.
- Calculating Speeds and Distances: If you travel at a speed of 48 km/h for 3 hours, the total distance covered is 48 x 3 = 144 km.
These are just a few examples, demonstrating the pervasive use of multiplication in daily life.
Expanding the Concept: Multiplication with Larger Numbers
The skills used to calculate 48 x 3 are directly applicable to more complex multiplication problems. The standard algorithm, distributive property, and other methods can be adapted for larger numbers. The understanding of place value and carrying over remains essential.
Consider a more complex example: 148 x 23. This can be broken down using the distributive property:
148 x 23 = 148 x (20 + 3) = (148 x 20) + (148 x 3) = 2960 + 444 = 3404
Or using the standard algorithm:
148
x 23
-------
444
2960
-------
3404
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the easiest way to learn multiplication?
A1: The easiest way involves consistent practice, starting with basic facts and gradually progressing to more complex calculations. Using visual aids, like manipulatives or drawings, can also significantly improve understanding. Utilizing different methods, like the distributive property, can make the process more engaging.
Q2: Are there any tricks to memorize multiplication tables?
A2: Yes, there are several mnemonic devices and tricks to aid memorization. These often involve patterns and relationships within the multiplication tables. Regular practice and repetition are key to mastering them.
Q3: How can I improve my multiplication skills?
A3: Practice is crucial. Start with smaller numbers and gradually increase the complexity. Use various methods to solve problems, and seek help when you encounter difficulties. Online resources and educational games can make learning more interactive and engaging.
Q4: Why is multiplication important?
A4: Multiplication is a fundamental mathematical operation used extensively in various fields, including science, engineering, finance, and everyday life. It simplifies calculations and allows us to solve problems involving repeated addition efficiently. A strong grasp of multiplication forms a basis for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Conclusion: Mastering Multiplication – A Building Block for Success
The seemingly simple calculation of 48 x 3 opens a door to a wide range of mathematical concepts and applications. By understanding the underlying principles, exploring different calculation methods, and recognizing its real-world relevance, we can appreciate the significance of multiplication. Mastering multiplication is not merely about memorizing facts; it's about developing a deeper understanding of mathematical relationships and building a strong foundation for future learning. From repeated addition to the distributive property and beyond, the journey of exploring 48 x 3 provides a valuable lesson in the power and elegance of mathematics. Continuous practice and a curious mindset will unlock further mathematical insights and empower you to confidently tackle more complex calculations.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 48 X 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.