40 Of 16
stanleys
Sep 12, 2025 · 6 min read
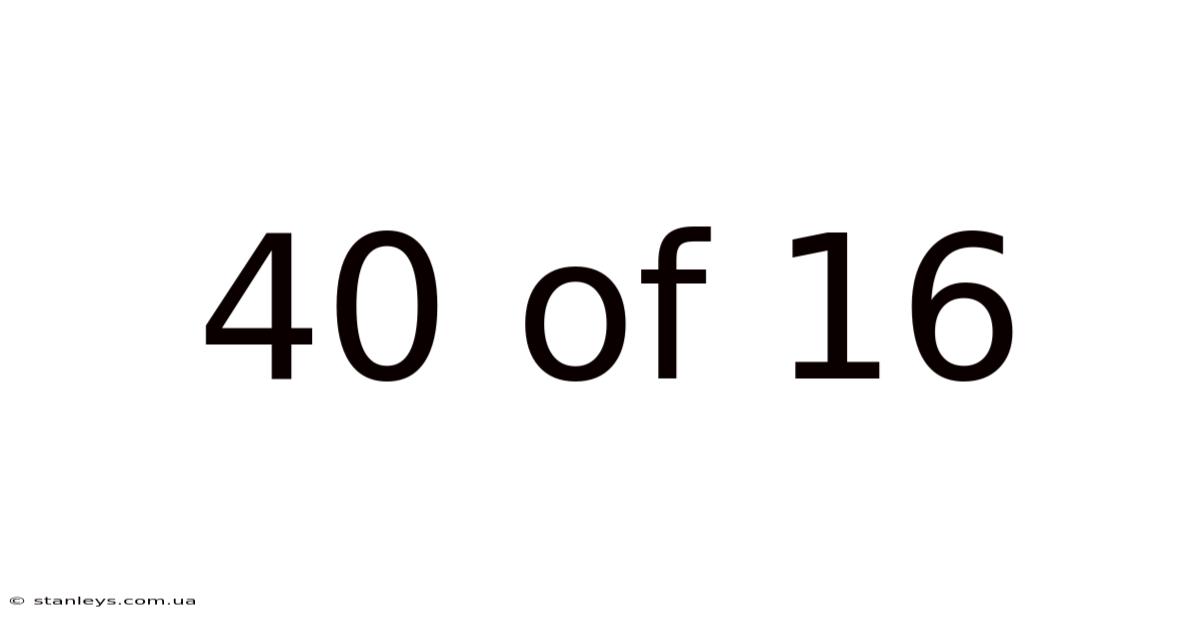
Table of Contents
Decoding 40 of 16: A Deep Dive into Probability, Odds, and Practical Applications
Understanding probability and odds is crucial in many aspects of life, from everyday decision-making to complex scientific calculations. This article delves into the seemingly simple concept of "40 of 16," exploring its meaning in the context of probability, calculating different odds representations, and illustrating its practical applications across various fields. We'll move beyond simple definitions to uncover the underlying mathematical principles and explore scenarios where understanding this ratio proves invaluable.
Introduction: What Does "40 of 16" Mean?
The phrase "40 of 16" represents a ratio or fraction – 40 out of a total of 16. At first glance, this seems illogical; you can't have 40 items out of only 16. This ratio, therefore, points towards a misunderstanding or a specific context where the numbers might represent something beyond a simple count of physical objects. We will explore various interpretations to understand what such a ratio might indicate, focusing primarily on its probabilistic implications. The keyword here is understanding the context, which will dramatically change the meaning and implications of this ratio.
Interpretations and Scenarios:
Several possibilities exist for what "40 of 16" might signify, depending on the context:
-
Incorrect Data: The most straightforward interpretation is that the numbers are incorrect or represent a data entry error. It's crucial to verify the source and accuracy of the data. If this ratio comes from a survey, experiment, or other data-gathering method, it warrants a review of the methodology.
-
Rate or Ratio, Not a Count: The numbers might represent a rate or ratio rather than a direct count of items. For instance:
-
Performance Metrics: Imagine a salesperson's performance: 40 successful sales calls out of 16 total calls attempted. While it seems improbable at first glance, this context makes it clear; the "40" might represent a cumulative success rate over a period, and "16" could be the number of attempts within a specific shorter time frame.
-
Event Frequency: "40" could represent the number of times an event occurred within a certain period, while "16" could represent the total number of opportunities for that event to occur.
-
-
Conditional Probability: The ratio might be expressing a conditional probability. In this case, the 40 and 16 represent events within a larger context, and the ratio signifies the probability of one event given the occurrence of another. Let's delve into this:
- A: Event 1 (e.g., rolling a six-sided die)
- B: Event 2 (e.g., getting a specific result after multiple die rolls)
- 40/16: might represent the conditional probability P(B|A) – the probability of Event B happening given that Event A already happened.
Calculating Probability and Odds:
Let's assume the "40 of 16" ratio represents a rate or frequency. To clarify, we need to understand how probability and odds are calculated and expressed:
-
Probability: Probability is a measure of the likelihood of an event occurring. It's expressed as a number between 0 and 1, inclusive. A probability of 0 means the event is impossible, and a probability of 1 means the event is certain. Probability is calculated as:
Probability = (Number of favorable outcomes) / (Total number of possible outcomes)In our case, assuming this is a rate, the probability is not 40/16, but rather would need re-interpretation based on the specific context. We could define the event as obtaining the outcome we count as 40, then dividing by the overall number of possibilities.
-
Odds: Odds represent the ratio of the probability of an event happening to the probability of it not happening. Odds are usually expressed as a ratio, such as "a to b" or "a:b." The odds in favor of an event are calculated as:
Odds in favor = (Probability of event) / (1 - Probability of event)And the odds against an event are:
Odds against = (1 - Probability of event) / (Probability of event)To calculate the odds from a given probability, we need to first identify the true probability based on the contextual interpretation of 40/16.
Practical Applications and Examples:
The "40 of 16" ratio, correctly interpreted, can find practical applications in many fields. Here are a few examples:
-
Sports Analytics: In baseball, a batting average of 0.250 (250 hits out of 1000 at-bats) is considered a good average. Similarly, other performance indicators in sports are often represented as ratios. The "40 of 16" could potentially represent, for example, the number of successful free throws made in a given number of attempts.
-
Quality Control: In manufacturing, quality control relies heavily on ratios and percentages. The ratio could represent the number of defective items found in a sample of items produced.
-
Financial Markets: Financial analysts use ratios and percentages to interpret market trends, assessing performance, risk factors, and future projections.
-
Medical Research: Medical research frequently utilizes ratios in clinical trials and epidemiological studies to analyze the efficacy of treatments and assess risk factors for certain diseases.
Addressing Potential Misinterpretations:
It’s crucial to avoid misinterpreting the "40 of 16" ratio without understanding its context. Simply stating that the probability is 40/16 = 2.5 is incorrect. Probabilities must be between 0 and 1. This emphasizes the critical importance of carefully reviewing the source of the data and understanding the underlying methodology.
Conclusion: The Importance of Context
The meaning of "40 of 16" is entirely dependent on its context. It’s not a simple probability calculation but rather a ratio that requires careful interpretation. Understanding the underlying meaning, whether it represents a rate, a conditional probability, or a simple data entry error, is essential. This highlights the critical need to analyze data critically and be aware of potential sources of error or misinterpretation. Always verify the source of your data, understand the methodology used to collect the data, and ensure that you interpret the ratio within its appropriate context.
FAQ:
-
Q: Can I calculate the probability directly as 40/16? A: No. Probability values must fall between 0 and 1. A value of 2.5 is impossible as a probability. You need to understand the context to determine the actual number of favorable outcomes and the total number of possible outcomes.
-
Q: What if the "40 of 16" represents a sample from a larger population? A: In this case, you would use statistical methods (like confidence intervals) to estimate the true proportion in the larger population. The simple ratio of 40/16 would be used as an initial estimate, but the uncertainty needs to be assessed via statistical tools.
-
Q: Are there any software tools that can help interpret this type of ratio? A: While no specific software is solely designed for interpreting "40 of 16," statistical software packages (like R or SPSS) can help analyze data, calculate probabilities and confidence intervals, and conduct statistical tests based on the context of the ratio.
-
Q: How can I avoid making similar misinterpretations in the future? A: Always question the source and methodology of your data. Ensure you understand the units and the context in which the ratio is presented. Be wary of ratios that seem illogical or impossible at face value. Always check for data entry errors and potential biases. Clearly define your events and outcomes before attempting any probability calculations.
This comprehensive analysis underscores the importance of carefully interpreting numerical data, especially ratios that initially appear paradoxical. By understanding the various contexts and methodologies involved, we can unlock the true meaning behind such data and apply it effectively across numerous fields. Remember, context is key!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
35 Of 120
Sep 12, 2025
-
20 Of 28
Sep 12, 2025
-
3 2 Km Miles
Sep 12, 2025
-
Mmhg En Pa
Sep 12, 2025
-
2 Of 300
Sep 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 40 Of 16 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.