32divided By 2
stanleys
Sep 14, 2025 · 6 min read
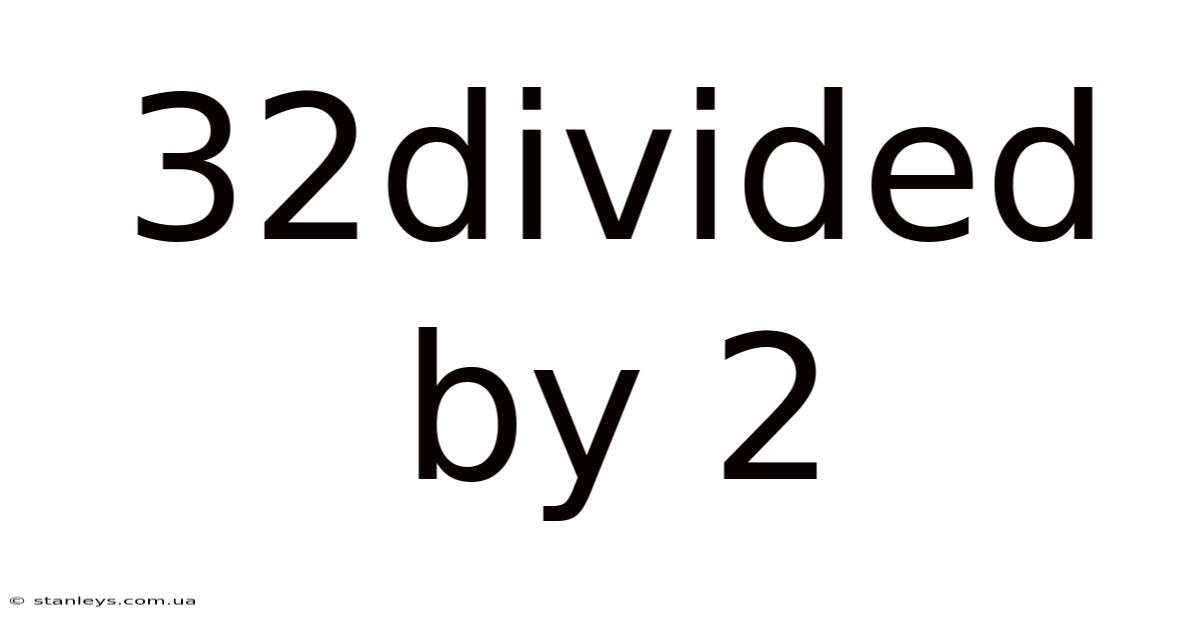
Table of Contents
32 Divided by 2: A Deep Dive into Simple Division and its Applications
This article explores the seemingly simple mathematical operation of 32 divided by 2, delving beyond the immediate answer to uncover the underlying principles, practical applications, and broader implications within mathematics and beyond. We'll examine different methods for solving this problem, explore its relevance in various fields, and address frequently asked questions. This comprehensive guide aims to enhance your understanding of division, a fundamental concept applicable across numerous areas of life.
Introduction: Understanding Division
Division is one of the four basic arithmetic operations, alongside addition, subtraction, and multiplication. It represents the process of splitting a quantity into equal parts or groups. In the expression "32 divided by 2," 32 is the dividend (the number being divided), 2 is the divisor (the number dividing the dividend), and the result is the quotient (the answer). Understanding these terms is crucial for grasping the fundamental concepts of division.
The question "32 divided by 2" can be written in several ways:
- 32 ÷ 2
- 32 / 2
- 32 over 2 (as a fraction)
Method 1: Repeated Subtraction
One way to solve 32 divided by 2 is through repeated subtraction. We repeatedly subtract the divisor (2) from the dividend (32) until we reach zero. The number of times we subtract is the quotient.
32 - 2 = 30 30 - 2 = 28 28 - 2 = 26 26 - 2 = 24 24 - 2 = 22 22 - 2 = 20 20 - 2 = 18 18 - 2 = 16 16 - 2 = 14 14 - 2 = 12 12 - 2 = 10 10 - 2 = 8 8 - 2 = 6 6 - 2 = 4 4 - 2 = 2 2 - 2 = 0
We subtracted 2 from 32 sixteen times. Therefore, 32 ÷ 2 = 16. While this method is conceptually simple and demonstrates the underlying meaning of division, it becomes cumbersome for larger numbers.
Method 2: Long Division
Long division is a more efficient algorithm for larger division problems. While seemingly complex, it's a systematic approach that breaks down the division process into manageable steps. For 32 divided by 2:
16
2 | 32
-2
12
-12
0
- We start by dividing the first digit of the dividend (3) by the divisor (2). 2 goes into 3 once (1), so we write 1 above the 3.
- We multiply the quotient (1) by the divisor (2), resulting in 2.
- We subtract 2 from 3, leaving 1.
- We bring down the next digit of the dividend (2), making it 12.
- We divide 12 by 2, which is 6. We write 6 above the 2.
- We multiply 6 by 2, resulting in 12.
- We subtract 12 from 12, leaving 0. There is no remainder.
Therefore, the quotient is 16.
Method 3: Multiplication and its Inverse Relationship with Division
Division and multiplication are inverse operations. This means that if we multiply the quotient by the divisor, we should get the dividend. In this case:
16 x 2 = 32
This confirms that our answer, 16, is correct. This inverse relationship is a powerful tool for checking your work and understanding the fundamental link between these two arithmetic operations.
Method 4: Halving
Since we are dividing by 2, we can also approach this problem by halving. Halving simply means dividing by 2. We can halve 32 to find the answer:
32 / 2 = 16
Practical Applications of Division: Beyond the Classroom
The seemingly simple operation of 32 divided by 2 has numerous practical applications across various fields:
-
Everyday Life: Sharing snacks equally amongst friends, calculating the cost per item when buying in bulk, splitting a bill at a restaurant, and determining the number of servings from a recipe all involve division.
-
Engineering and Construction: Calculations involving area, volume, and material quantities frequently require division. For example, determining the number of bricks needed to build a wall of a certain size involves dividing the total area by the area of a single brick.
-
Computer Science: Division plays a critical role in algorithms, data structures, and memory management. Many programming tasks involve dividing data into smaller chunks or allocating resources efficiently.
-
Finance: Calculating interest rates, determining profit margins, and splitting investments all rely on division.
-
Science: Numerous scientific calculations, such as determining average values, calculating concentrations, and converting units, require division.
-
Cooking and Baking: Scaling recipes up or down involves dividing or multiplying ingredient quantities.
The Concept of Remainders
While 32 divided by 2 results in a whole number (16) with no remainder, many division problems do have remainders. A remainder is the amount left over after the division is complete. For example, if we divide 33 by 2:
33 ÷ 2 = 16 with a remainder of 1
This can be expressed as 16 R 1 or 16 1/2 (16 and a half). Understanding remainders is essential for various applications, including calculating averages and dealing with situations where perfect division isn't possible.
Exploring Further: Fractions and Decimals
The problem can also be represented as a fraction: 32/2. This fraction simplifies to 16/1, which is equivalent to 16. This highlights the connection between division and fractions. Division also plays a crucial role in converting fractions to decimals. For example, the fraction 1/2 is equivalent to the decimal 0.5, obtained by dividing 1 by 2.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Q: What is the opposite of division?
- A: Multiplication.
-
Q: Can you divide by zero?
- A: No, division by zero is undefined in mathematics. It leads to an infinite result and is mathematically impossible.
-
Q: What if I want to divide 32 by a number other than 2?
- A: The process remains the same. You would apply the same methods (repeated subtraction, long division, etc.) using the new divisor.
-
Q: How does division relate to other mathematical operations?
- A: Division is closely related to multiplication (inverse operation), addition (repeated subtraction), and fractions (representation).
Conclusion: The Significance of Simple Division
While the division of 32 by 2 might seem trivial at first glance, a deeper examination reveals the fundamental importance of this operation within mathematics and its widespread practical applications. Understanding the various methods for solving this problem, along with the concepts of remainders, fractions, and decimals, provides a solid foundation for tackling more complex mathematical challenges. From everyday tasks to advanced scientific calculations, the ability to perform division accurately and efficiently is a crucial skill that transcends the boundaries of the classroom. The seemingly simple answer, 16, represents much more than just a numerical result; it represents a gateway to understanding a foundational building block of mathematics. Mastering this concept opens doors to countless opportunities for further exploration and application within various fields of study and everyday life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Address Book Uk
Sep 14, 2025
-
112 Kg Pounds
Sep 14, 2025
-
62lb In Stone
Sep 14, 2025
-
Latitude Montreal Canada
Sep 14, 2025
-
45km To Miles
Sep 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 32divided By 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.