3.2 M Cm
stanleys
Sep 21, 2025 · 6 min read
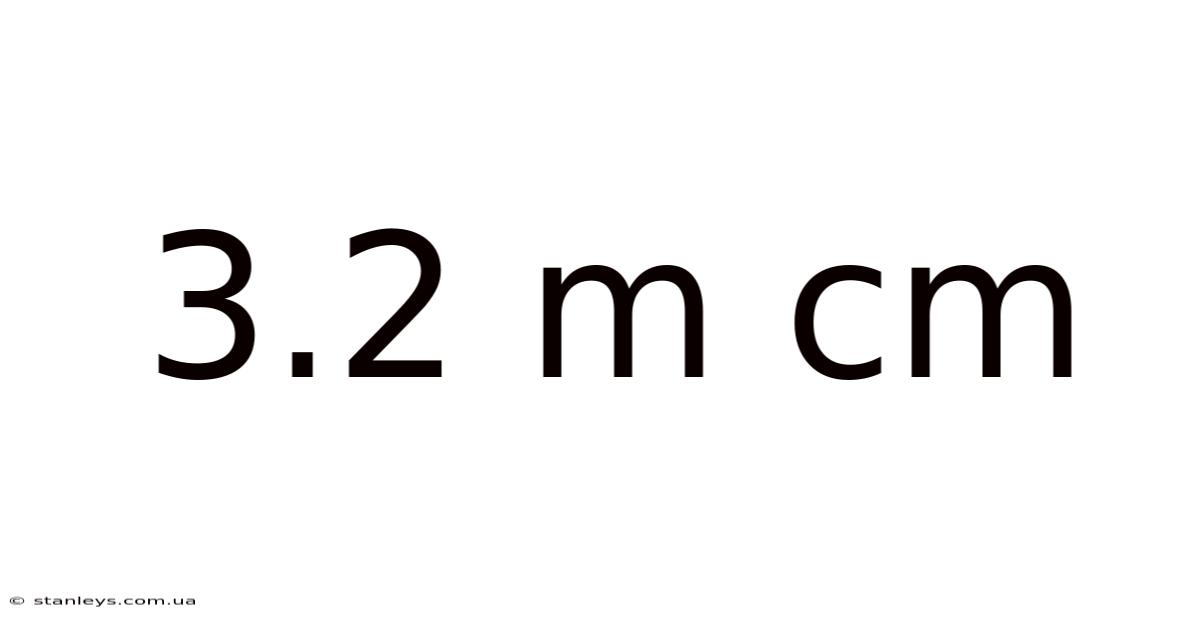
Table of Contents
Decoding 3.2 m cm: A Comprehensive Guide to Metric Conversions and Applications
Understanding metric conversions is crucial in numerous fields, from everyday life to advanced scientific research. This article delves deep into the meaning and implications of "3.2 m cm," clarifying the potential ambiguity and exploring its applications across various disciplines. We'll navigate the complexities of unit conversions, provide practical examples, and address frequently asked questions, ensuring a comprehensive understanding for readers of all backgrounds.
Introduction: The Ambiguity of 3.2 m cm
The expression "3.2 m cm" presents a slight ambiguity. At first glance, it appears to be a measurement combining meters (m) and centimeters (cm). However, the lack of a clear separator or operator leaves room for interpretation. Does it represent 3.2 meters and a certain number of centimeters, or is it an attempt to represent a single measurement in a combined unit format? This ambiguity highlights the importance of precise notation in scientific and engineering contexts. We'll explore both potential interpretations and offer guidance on avoiding such ambiguity in the future.
Interpretation 1: 3.2 Meters and an Unknown Number of Centimeters
This interpretation assumes "3.2 m cm" signifies a measurement of 3.2 meters plus an unspecified number of centimeters. This is an incomplete expression and lacks the precision needed for accurate calculations or measurements. To clarify, we need additional information regarding the number of centimeters. For example, a more complete expression could be "3.2 m and 5 cm" or "3.2 m and 15 cm," which would represent different total lengths.
Interpretation 2: 3.2 Meters Converted to Centimeters
A more plausible interpretation, although still imprecisely stated, is that "3.2 m cm" attempts to represent 3.2 meters expressed in centimeters. This requires a unit conversion. Since 1 meter equals 100 centimeters, we can perform the following conversion:
- 3.2 meters * 100 centimeters/meter = 320 centimeters
Therefore, in this context, "3.2 m cm" could be understood (though incorrectly written) as representing 320 centimeters. The crucial point here is the understanding that proper notation in measurements is paramount. The correct way to express this measurement would simply be "320 cm" or "3.2 m."
Understanding Metric Prefixes and Unit Conversions
The metric system, also known as the International System of Units (SI), is based on powers of 10, making conversions relatively straightforward. Understanding metric prefixes is essential for navigating these conversions effectively. Here's a table outlining some common prefixes:
| Prefix | Symbol | Multiplier |
|---|---|---|
| kilo | k | 10<sup>3</sup> (1000) |
| hecto | h | 10<sup>2</sup> (100) |
| deca | da | 10<sup>1</sup> (10) |
| deci | d | 10<sup>-1</sup> (0.1) |
| centi | c | 10<sup>-2</sup> (0.01) |
| milli | m | 10<sup>-3</sup> (0.001) |
Practical Applications of Metric Measurements
Metric measurements are ubiquitous in various fields:
- Construction and Engineering: Lengths, widths, and heights of buildings, roads, and other structures are often expressed in meters and centimeters. Accurate conversions are critical for precise planning and execution.
- Manufacturing: The production of components requires precise measurements. Tolerances are often specified in millimeters or micrometers.
- Science and Research: Scientific experiments rely on accurate measurements of mass, volume, and length. The metric system provides a consistent and standardized framework for these measurements.
- Everyday Life: Many everyday items, from clothing sizes to food packaging, utilize metric units. Understanding these units helps in making informed decisions regarding purchases and everyday tasks.
Examples of Metric Conversions
Let's examine some practical examples involving metric unit conversions:
- Converting Meters to Centimeters: If a table measures 2.5 meters in length, its length in centimeters is 2.5 m * 100 cm/m = 250 cm.
- Converting Centimeters to Millimeters: A screw measures 15 centimeters in length. Its length in millimeters is 15 cm * 10 mm/cm = 150 mm.
- Converting Kilometers to Meters: A journey covers 5 kilometers. The distance in meters is 5 km * 1000 m/km = 5000 m.
Avoiding Ambiguity in Metric Notation
To avoid the ambiguity seen in the original "3.2 m cm" expression, follow these guidelines:
- Use a Decimal Point: If combining meters and centimeters, use a decimal point to represent the combined measurement in a single unit (e.g., 3.25 m, which is equivalent to 3 meters and 25 centimeters).
- Use Clear Separators: If representing distinct measurements, use words such as "and" or utilize separate notations with units clearly indicated (e.g., "3.2 m and 15 cm").
- Choose a Single Unit: For clarity and consistency, strive to express measurements using a single unit whenever possible.
Advanced Applications: Volume and Area Calculations
The metric system extends beyond linear measurements to encompass volume and area calculations.
- Area: Area is typically expressed in square meters (m²) or square centimeters (cm²). Converting between these units involves squaring the conversion factor. For example, 1 m² = (100 cm)² = 10000 cm².
- Volume: Volume is often expressed in cubic meters (m³) or cubic centimeters (cm³). Converting between these units involves cubing the conversion factor. For instance, 1 m³ = (100 cm)³ = 1000000 cm³.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the difference between meters and centimeters?
- A: A meter (m) is a fundamental unit of length in the metric system. A centimeter (cm) is 1/100th of a meter.
-
Q: How do I convert kilometers to millimeters?
- A: First, convert kilometers to meters (multiply by 1000). Then, convert meters to centimeters (multiply by 100), and finally, convert centimeters to millimeters (multiply by 10). Alternatively, multiply the initial number of kilometers by 1,000,000.
-
Q: Why is it important to use precise notation in metric measurements?
- A: Precise notation avoids ambiguity and ensures accurate calculations and communication, particularly in technical fields where even small errors can have significant consequences.
-
Q: Are there any other important metric units beyond meters and centimeters?
- A: Yes, many others exist, including millimeters, kilometers, micrometers, nanometers, etc., each suitable for different scales of measurement.
Conclusion: Mastering Metric Conversions
Understanding the nuances of metric conversions, particularly the relationship between meters and centimeters, is fundamental to accurate measurement and calculation. This article has clarified the ambiguity surrounding "3.2 m cm," emphasized the importance of precise notation, and provided a thorough overview of practical applications and unit conversions within the metric system. By applying the principles outlined here, one can confidently navigate the world of metric measurements, contributing to greater accuracy and precision across various fields. Remember, clarity and precision in scientific and technical communication are paramount, and consistent use of proper units is crucial for effective understanding and avoiding potential errors.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 3.2 M Cm . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.