2x 7 13
stanleys
Sep 16, 2025 · 6 min read
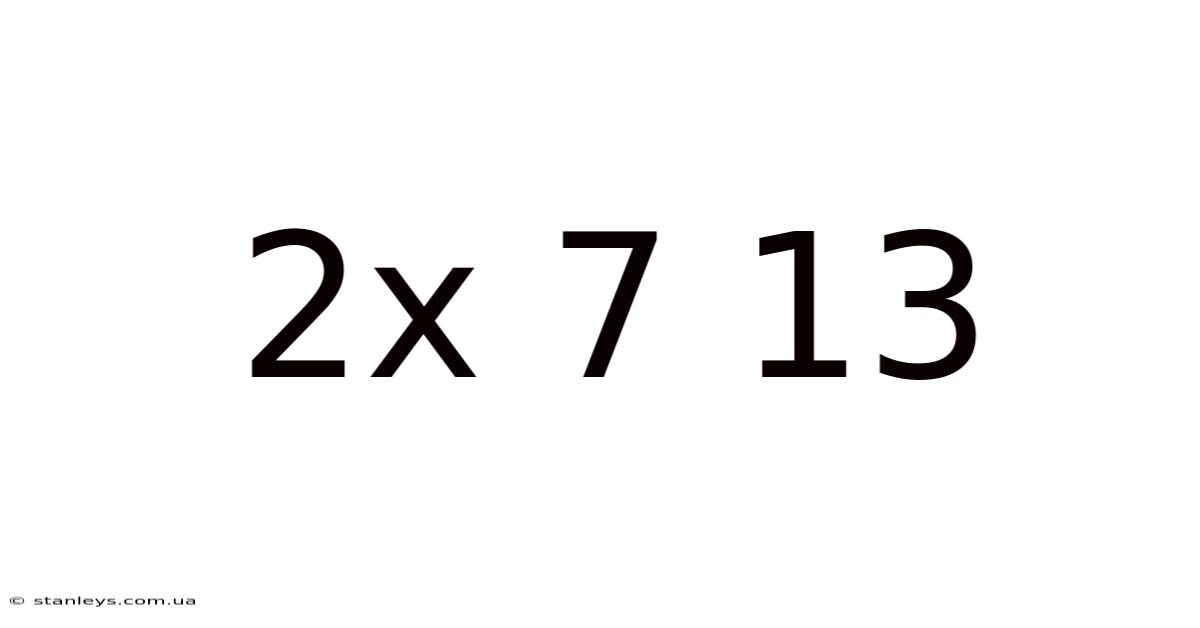
Table of Contents
Unraveling the Mystery of 2x7=13: A Deep Dive into Mathematical Illusions and Cognitive Biases
The equation "2 x 7 = 13" is, of course, incorrect. Basic arithmetic dictates that 2 multiplied by 7 equals 14. However, presenting this seemingly simple falsehood opens a fascinating door into the world of mathematical illusions, cognitive biases, and the very nature of how we perceive and process information. This article will explore not only why this equation is wrong but also delve into the psychological factors that might lead someone to accept it as true, examining the broader implications for education, critical thinking, and the spread of misinformation.
Introduction: The Allure of the Incorrect
The statement "2 x 7 = 13" acts as a powerful illustration of how easily our minds can be misled, even with something as seemingly straightforward as multiplication. It highlights the vulnerability of our cognitive processes to various biases and the importance of critical thinking and verification. This seemingly simple error can serve as a springboard for a deeper understanding of mathematical reasoning, the limitations of human perception, and the methods used to create and disseminate misinformation. We will investigate why this incorrect equation might seem plausible to some, explore related cognitive biases, and discuss the implications of such errors in various contexts.
Why 2 x 7 ≠ 13: A Basic Mathematical Refresher
At its core, the statement's inaccuracy stems from a fundamental misunderstanding of multiplication. Multiplication is repeated addition. 2 x 7 means adding the number 7 to itself twice: 7 + 7 = 14. There's no mathematical operation or alternative interpretation that would legitimately result in 13. This foundational mathematical principle forms the bedrock of more complex calculations and equations. Any deviation from this principle, as seen in the equation "2 x 7 = 13," represents a clear error.
Cognitive Biases and the Acceptance of Falsehoods
The question then becomes: why might someone believe such an obvious falsehood? Several cognitive biases could play a significant role:
-
Confirmation Bias: This bias leads individuals to favor information that confirms their pre-existing beliefs and to reject information that contradicts them. If someone holds a belief – perhaps stemming from a misunderstanding of mathematics or a desire to believe a specific narrative – they might be more likely to accept "2 x 7 = 13" if it aligns with that belief, even if presented with contradictory evidence.
-
Availability Heuristic: This cognitive shortcut involves judging the likelihood of an event based on how easily examples come to mind. If someone has recently encountered information (real or fabricated) that appears to support "2 x 7 = 13," they might incorrectly judge it as more likely to be true.
-
Bandwagon Effect: The tendency to adopt beliefs and behaviors simply because many other people do so can also contribute. If a significant group of people, especially those perceived as authoritative figures, promote this false equation, others might be swayed to believe it as well.
-
Authority Bias: We tend to trust information from sources we perceive as authoritative. If a person of perceived authority (a teacher, a celebrity, etc.) presented "2 x 7 = 13," the authority bias could lead to uncritical acceptance.
-
Cognitive Dissonance: This describes the mental discomfort experienced when holding conflicting beliefs. If someone believes a certain narrative that requires accepting "2 x 7 = 13," they might experience cognitive dissonance if they acknowledge the correct answer. To reduce this discomfort, they might unconsciously rationalize the falsehood or reject the correct information.
The Role of Misinformation and its Spread
The equation "2 x 7 = 13" can serve as a microcosm of the broader problem of misinformation spread online and offline. The ease with which false information can be disseminated through social media and other channels is alarming. Understanding the cognitive biases that make people susceptible to such misinformation is crucial in combatting its spread. The simple falsehood of this mathematical equation underscores the need for critical evaluation of information and the development of media literacy skills.
Implications for Education and Critical Thinking
The prevalence of such mathematical illusions highlights the importance of strong mathematical foundations in education. A thorough understanding of basic arithmetic principles is essential in developing critical thinking skills. Students need to be taught not just the "what" of mathematics (the procedures and calculations), but also the "why" – the underlying logic and reasoning that makes mathematical principles work. Encouraging questioning, critical analysis, and independent verification of information should be core components of any effective mathematics curriculum. This approach can help students develop a more robust understanding of mathematics and enhance their ability to discern accurate information from falsehoods.
Debunking the Myth: Verification and Proof
The most effective way to counter the falsehood of "2 x 7 = 13" is through direct verification. This might involve:
- Repeated Addition: Physically counting objects or using a visual representation to demonstrate that adding 7 twice results in 14.
- Using a Calculator: Employing a calculator to perform the calculation provides a quick and unambiguous result.
- Referencing Mathematical Textbooks or Resources: Consulting reliable sources confirms the established rules of multiplication.
These methods provide concrete evidence to disprove the falsehood and reinforce the correct understanding of multiplication.
Expanding the Understanding: Beyond Simple Multiplication
While the focus is on the simple equation "2 x 7 = 13," the principles discussed extend far beyond this basic example. Similar cognitive biases can influence our understanding of more complex mathematical concepts, scientific theories, and even social and political issues. The ability to critically evaluate information, identify biases, and verify claims remains crucial in navigating the complexities of the modern world. Developing strong critical thinking skills is therefore paramount in becoming an informed and responsible citizen.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Why is this equation so compelling to some? A: The equation's deceptiveness lies in its simplicity. It plays on the assumption that mathematical truths are self-evident, making it more likely for individuals to accept it uncritically, especially if influenced by cognitive biases or misinformation.
-
Q: How can I prevent myself from falling for similar mathematical fallacies? A: Develop a habit of verification. Always double-check results, especially if they seem counterintuitive or unexpected. Refer to reliable sources and utilize tools like calculators to confirm calculations.
-
Q: Are there similar illusions in other areas of study? A: Absolutely. Cognitive biases affect decision-making across all fields. Illusions and logical fallacies are prevalent in fields such as statistics, logic, and even everyday reasoning. Developing critical thinking skills is key to identifying and avoiding these traps.
-
Q: Is it important to debunk these types of errors? A: Yes, it's crucial. Debunking mathematical errors and misconceptions helps reinforce correct understanding, promotes critical thinking, and protects against the spread of misinformation. This is especially important in education and public discourse.
Conclusion: The Importance of Critical Thinking in a World of Information Overload
The deceptively simple equation "2 x 7 = 13" serves as a potent reminder of the importance of critical thinking and the vulnerability of human cognition to bias and misinformation. While the equation itself is demonstrably false, its power lies in its ability to highlight the underlying cognitive mechanisms that can lead individuals to accept false information. Understanding these mechanisms is paramount in navigating the overwhelming flow of information in the modern world. By promoting critical thinking, mathematical literacy, and media awareness, we can equip individuals with the skills necessary to discern truth from falsehood and make informed decisions. This goes far beyond the realm of simple arithmetic; it underpins the ability to navigate complex information, challenge assumptions, and ultimately, to build a more informed and rational society.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2x 7 13 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.