21 Of 320
stanleys
Sep 21, 2025 · 6 min read
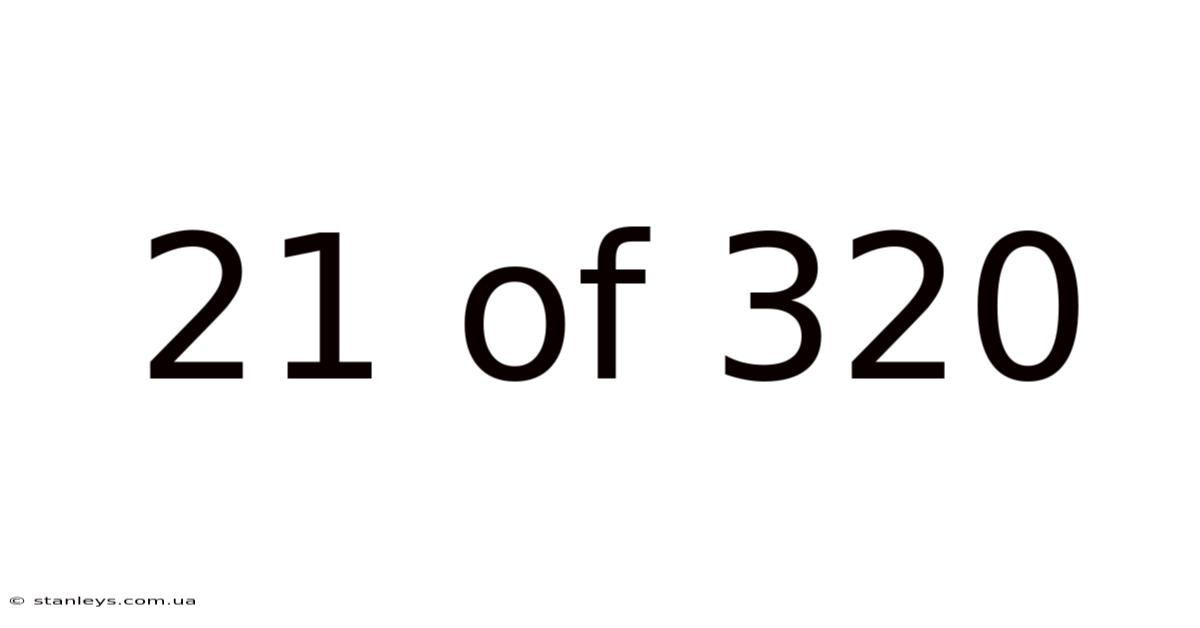
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery: Understanding the Significance of 21 out of 320
The seemingly simple fraction, 21 out of 320, or 21/320, might initially appear insignificant. However, depending on the context, this ratio can hold significant weight, revealing important information about probabilities, percentages, or even performance metrics. This article delves into the various interpretations and applications of this ratio, exploring its mathematical significance and practical implications across different fields. We'll unpack how to calculate its percentage equivalent, its implications in statistics, and its potential use in diverse scenarios ranging from business analysis to scientific research.
Understanding the Basic Calculation: Percentage and Ratio
Before we delve into the complexities, let's establish the fundamental mathematical concepts. The ratio 21/320 represents a part-to-whole relationship. 21 represents a specific number of successes, occurrences, or instances, while 320 represents the total number of possibilities or attempts. To convert this ratio into a more readily understandable format, we need to calculate the percentage. This is done by dividing the part (21) by the whole (320) and multiplying the result by 100:
(21 / 320) * 100 = 6.5625%
Therefore, 21 out of 320 represents approximately 6.56%. This percentage provides a concise summary of the ratio, making it easier to compare and interpret in various contexts.
Contextualizing the Ratio: Practical Applications
The significance of 21/320 heavily depends on its context. Let's explore some potential scenarios:
-
Business Performance: Imagine a company launching a new marketing campaign. If 21 out of 320 potential customers responded positively, this 6.56% conversion rate provides crucial information about campaign effectiveness. This data point can then be used to refine strategies, optimize messaging, or allocate resources more efficiently. Low conversion rates might signal the need for A/B testing, market research, or a complete overhaul of the campaign.
-
Survey Results: If a survey of 320 individuals reveals that 21 support a particular policy, the 6.56% support rate provides valuable insights into public opinion. This information is crucial for policymakers, researchers, and organizations interested in gauging public sentiment on a given issue. Further analysis might involve investigating demographic factors to better understand the distribution of support.
-
Quality Control: In manufacturing, if 21 out of 320 products fail quality control, this 6.56% defect rate indicates potential issues within the production process. This information triggers investigations into the causes of defects, leading to improvements in manufacturing techniques, material sourcing, or quality assurance protocols. Continuous monitoring of defect rates is essential for maintaining high product quality and customer satisfaction.
-
Scientific Research: In scientific experiments, the ratio might represent the success rate of a particular procedure or the prevalence of a specific characteristic within a sample population. Statistical analysis is crucial here to determine if the observed rate is statistically significant or merely due to chance. Factors like sample size and confidence intervals must be considered to draw reliable conclusions.
-
Healthcare: Consider a clinical trial where 21 out of 320 patients responded positively to a new treatment. This 6.56% response rate is important for determining the efficacy of the treatment. Further research, including larger sample sizes and rigorous statistical analysis, is needed to validate the results and ensure their clinical significance.
Deeper Dive into Statistical Significance
The simple percentage (6.56%) only tells part of the story. To fully understand the significance of 21 out of 320, we need to consider statistical analysis. Here are some key aspects:
-
Confidence Intervals: A confidence interval provides a range within which the true population proportion likely lies. For example, a 95% confidence interval might suggest that the true proportion of successes lies between 3% and 10%. This accounts for sampling error and provides a more nuanced understanding of the results.
-
Hypothesis Testing: Hypothesis testing allows us to determine if the observed result (21 out of 320) is statistically significant or simply due to random chance. This involves formulating a null hypothesis (e.g., there is no difference between the observed rate and a hypothesized rate) and testing it against the observed data. The p-value derived from this test indicates the probability of observing the result if the null hypothesis is true. A low p-value (typically below 0.05) suggests that the null hypothesis can be rejected, indicating statistical significance.
-
Sample Size: The sample size (320 in this case) plays a crucial role in the reliability of the results. Larger sample sizes generally lead to more precise estimates and narrower confidence intervals. A smaller sample size might yield results that are less reliable and more susceptible to sampling error.
-
Margin of Error: The margin of error is a measure of the uncertainty associated with the estimate. It represents the range within which the true population proportion is likely to fall. A larger sample size results in a smaller margin of error, indicating greater accuracy.
Exploring Further Analysis Techniques
Several statistical methods can be applied to analyze the 21/320 ratio further depending on the context and the research questions. These might include:
-
Chi-square test: This test assesses the association between categorical variables. It can be used to determine whether there's a statistically significant relationship between two or more categorical variables. For example, if we want to determine if there is a significant association between the response (21/320) and a demographic variable like age or gender.
-
Regression analysis: If the ratio is part of a larger dataset containing other variables, regression analysis can help determine the relationship between the ratio and these other variables. This allows for prediction and understanding of factors influencing the 21/320 outcome.
-
Bayesian analysis: This method allows for incorporating prior knowledge and beliefs into the analysis, leading to more informed inferences about the 21/320 ratio. It is particularly useful when prior information is available or when dealing with small sample sizes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: How do I calculate the confidence interval for 21/320? A: Calculating confidence intervals requires using statistical software or specialized calculators. The inputs needed are the sample size (320), the number of successes (21), and the desired confidence level (e.g., 95%).
-
Q: What if my sample size is smaller? A: Smaller sample sizes lead to wider confidence intervals and less precise estimates. The results might be less reliable and more susceptible to sampling error.
-
Q: How do I interpret a low p-value? A: A low p-value (typically below 0.05) suggests that the observed result is statistically significant and unlikely to have occurred by chance alone. It indicates that you can reject the null hypothesis.
-
Q: What if my data doesn't follow a normal distribution? A: If the data doesn't follow a normal distribution, non-parametric statistical methods might be more appropriate.
Conclusion: The Importance of Context and Further Analysis
The ratio 21 out of 320, while seemingly simple, holds significant potential for interpretation and analysis. Its precise meaning depends entirely on the context in which it's presented. While the simple percentage calculation provides a quick overview (approximately 6.56%), a deeper understanding requires exploring statistical significance through confidence intervals, hypothesis testing, and other relevant statistical techniques. The sample size and the underlying distribution of the data also heavily influence the interpretation. Always remember that context, further analysis, and the right statistical approach are crucial to unlocking the true meaning and implications of this, or any similar, ratio. The seemingly simple fraction can be a powerful tool for informed decision-making across various fields, provided it's analyzed with the appropriate care and statistical rigor.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 21 Of 320 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.