2.5 Of 3000
stanleys
Sep 21, 2025 · 5 min read
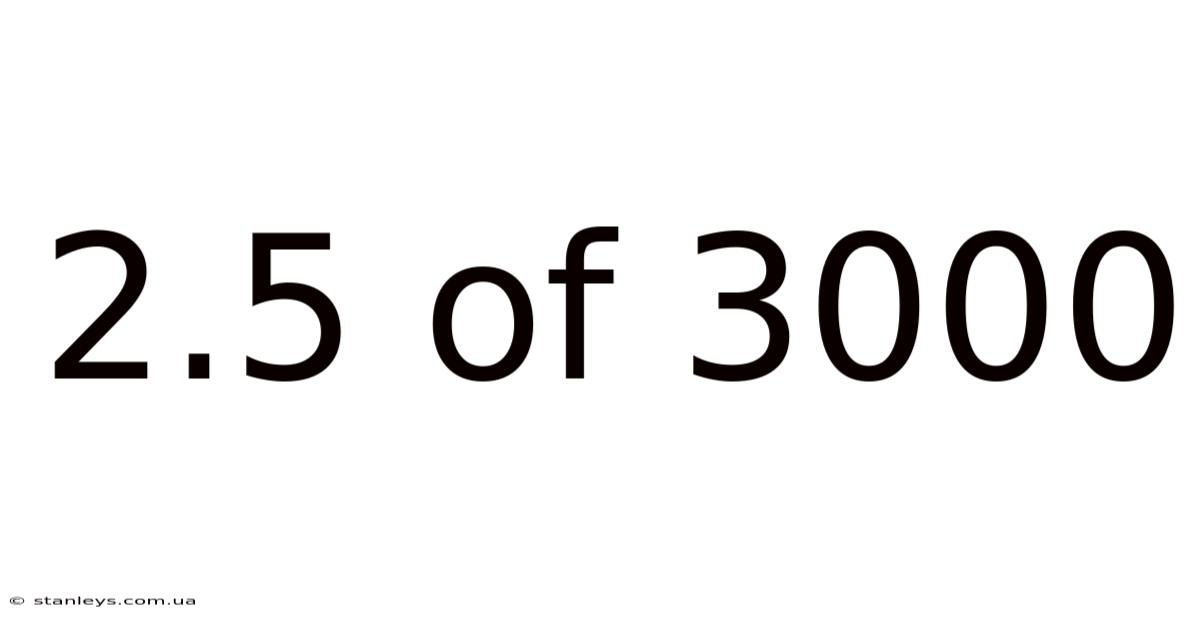
Table of Contents
Understanding 2.5 out of 3000: Fractions, Percentages, and Real-World Applications
This article explores the meaning of "2.5 out of 3000," demonstrating how to represent this value as a fraction, a percentage, and understanding its implications within various contexts. We'll delve into the calculations, explore the significance of such a small fraction in larger datasets, and discuss real-world applications where such comparisons are relevant. Understanding this concept is crucial in fields ranging from statistics and data analysis to finance and everyday problem-solving.
What Does 2.5 out of 3000 Mean?
At its core, "2.5 out of 3000" represents a part of a whole. The whole is 3000, and 2.5 is the part we're interested in. This immediately suggests the use of fractions and percentages to express the proportion. This type of comparison is frequently encountered in various scenarios, such as:
- Statistical Analysis: Analyzing survey responses, experimental results, or demographic data often involves comparing small subsets to the larger population.
- Financial Modeling: Evaluating investment returns, assessing risk, or calculating probabilities involves working with proportions and percentages.
- Quality Control: Determining the defect rate in a manufacturing process relies on comparing the number of defective items to the total number produced.
- Academic Performance: Understanding one's grade in a class often necessitates considering the number of points earned out of the total points possible.
Converting to a Fraction
The most straightforward way to represent 2.5 out of 3000 is as a fraction: 2.5/3000. However, fractions are generally expressed with whole numbers in the numerator and denominator. To achieve this, we can multiply both the numerator and the denominator by 2 to eliminate the decimal:
(2.5 * 2) / (3000 * 2) = 5/6000
This fraction can be further simplified by finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of 5 and 6000, which is 5. Dividing both the numerator and the denominator by 5 gives us:
5/6000 = 1/1200
Therefore, 2.5 out of 3000 is equivalent to the fraction 1/1200. This simplified form provides a clearer representation of the proportion.
Converting to a Percentage
To express 2.5 out of 3000 as a percentage, we first convert the fraction to a decimal by dividing the numerator by the denominator:
1 / 1200 = 0.0008333...
To convert this decimal to a percentage, we multiply by 100:
0.0008333... * 100 = 0.08333...%
Rounding to a reasonable number of decimal places, we get approximately 0.08%. This signifies that 2.5 represents a very small proportion (less than one-tenth of one percent) of the total 3000.
Understanding the Significance of Small Fractions
The small percentage (0.08%) highlights the relative insignificance of 2.5 compared to 3000. In many contexts, such a small fraction might be considered negligible. However, the significance depends entirely on the context.
Consider these examples:
- Context 1: Number of Defective Items: If 2.5 out of 3000 manufactured items are defective, this represents a very low defect rate (0.08%). This might be considered acceptable depending on industry standards.
- Context 2: Survey Responses: If 2.5 out of 3000 survey respondents chose a particular option, this suggests limited support for that option. The small number might prompt further investigation into the reasons behind the low response rate.
- Context 3: Financial Investments: If an investment resulted in a gain of 2.5 units out of an initial investment of 3000 units, this represents a very small return on investment (ROI). The low ROI might indicate a poor investment strategy.
Real-World Applications and Examples
The concept of comparing a small number to a larger whole finds application in numerous areas:
- Public Health: Tracking the incidence of a rare disease. A small number of cases compared to the total population illustrates the rarity of the disease.
- Environmental Science: Monitoring pollution levels. A small amount of pollutant in a large water body might still pose a risk, depending on the type of pollutant and its concentration.
- Market Research: Analyzing customer preferences. A small percentage of customers choosing a particular product might indicate a need for product improvement or targeted marketing.
- Sports Statistics: Calculating batting averages or shooting percentages. A small number of successful attempts compared to the total number of attempts reflects the player's performance.
Mathematical Considerations and Further Explorations
While we've focused on the basic calculations and interpretations, there are more advanced mathematical concepts that can be applied:
- Standard Error: When dealing with samples (like survey responses), understanding the standard error helps determine the confidence interval for the estimate. This is crucial for making inferences about the population based on the sample.
- Hypothesis Testing: Statistical hypothesis testing allows us to determine whether the observed proportion (0.08%) is significantly different from a hypothesized value (e.g., 0%).
- Regression Analysis: If the 2.5 value is part of a larger dataset with other variables, regression analysis can explore the relationship between 2.5 and other factors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can I use a calculator to perform these calculations?
A: Absolutely! Calculators are invaluable for converting fractions to decimals and percentages, especially when dealing with larger numbers.
Q: What if the number wasn't 2.5 but a different decimal?
A: The process remains the same. You would express the number as a fraction, simplify it, and then convert it to a percentage using the same steps.
Q: How do I know when to round the percentage?
A: Rounding depends on the context. In many situations, rounding to two or three decimal places is sufficient. However, for precise scientific or financial calculations, more decimal places might be necessary.
Q: What if the initial number was not 3000 but another large number?
A: The principles remain identical. You will simply substitute the new large number in place of 3000 and follow the same steps of converting to a fraction and then to a percentage.
Conclusion
Understanding the meaning and implications of "2.5 out of 3000" involves translating it into more readily interpretable forms like fractions and percentages. While seemingly simple, this concept has broad applications across many disciplines. Understanding the relative proportion, the conversion process, and the context in which the comparison is made are crucial for accurate interpretation and informed decision-making. The small percentage (0.08%) itself does not inherently signify success or failure; its interpretation hinges completely on the context within which it appears. This emphasizes the importance of considering the broader picture and applying appropriate statistical methods when dealing with proportions and percentages in real-world applications.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2.5 Of 3000 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.