15 Of 850
stanleys
Sep 21, 2025 · 7 min read
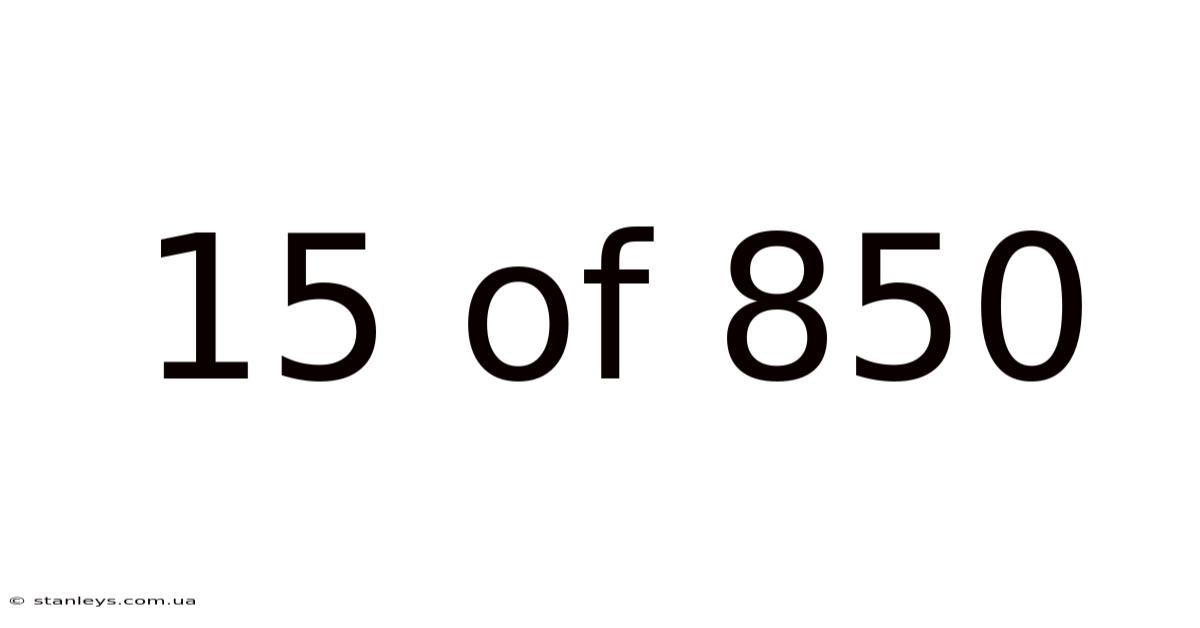
Table of Contents
Unlocking the Mysteries of 15/850: A Deep Dive into Fraction Simplification and its Applications
Understanding fractions is a fundamental skill in mathematics, forming the building blocks for more advanced concepts. While seemingly simple, the manipulation and interpretation of fractions can present challenges. This article will delve into the specific fraction 15/850, exploring its simplification, practical applications, and the broader mathematical principles it exemplifies. We will cover the process of finding the greatest common divisor (GCD), explore real-world scenarios where this fraction might arise, and address common misconceptions surrounding fraction reduction.
Understanding Fractions: A Quick Refresher
Before diving into the specifics of 15/850, let's refresh our understanding of fractions. A fraction represents a part of a whole. It's expressed as a ratio of two numbers: the numerator (the top number) and the denominator (the bottom number). The numerator indicates how many parts we have, while the denominator indicates the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into. For instance, in the fraction 3/4, 3 is the numerator and 4 is the denominator. This represents 3 out of 4 equal parts.
Simplifying Fractions: The Core Concept
Simplifying a fraction, also known as reducing a fraction to its simplest form, means expressing the fraction with the smallest possible whole numbers in the numerator and denominator. This is achieved by finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of both numbers and dividing both the numerator and denominator by it. The GCD is the largest number that divides both the numerator and denominator without leaving a remainder.
Finding the GCD of 15 and 850
To simplify 15/850, we need to find the GCD of 15 and 850. There are several methods to achieve this:
-
Listing Factors: List all the factors of both 15 and 850. The largest number common to both lists is the GCD. The factors of 15 are 1, 3, 5, and 15. The factors of 850 are 1, 2, 5, 10, 17, 25, 34, 50, 85, 170, 425, and 850. The largest common factor is 5.
-
Prime Factorization: Express both numbers as a product of their prime factors. The GCD is the product of the common prime factors raised to the lowest power. The prime factorization of 15 is 3 x 5. The prime factorization of 850 is 2 x 5² x 17. The common prime factor is 5, and the lowest power is 5¹, so the GCD is 5.
-
Euclidean Algorithm: This is a more efficient method for larger numbers. It involves repeatedly applying the division algorithm until the remainder is 0. The last non-zero remainder is the GCD.
- Divide 850 by 15: 850 = 15 x 56 + 10
- Divide 15 by the remainder 10: 15 = 10 x 1 + 5
- Divide 10 by the remainder 5: 10 = 5 x 2 + 0
The last non-zero remainder is 5, so the GCD of 15 and 850 is 5.
Simplifying 15/850
Now that we know the GCD is 5, we can simplify the fraction:
15/850 = (15 ÷ 5) / (850 ÷ 5) = 3/170
Therefore, the simplest form of 15/850 is 3/170.
Real-World Applications of Fraction Simplification
Simplifying fractions isn't just an abstract mathematical exercise; it has numerous practical applications in various fields:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often require precise measurements. Simplifying fractions ensures accurate proportions when adjusting recipes. For instance, if a recipe calls for 15/850 of a cup of sugar and you need to halve the recipe, simplifying the fraction makes the calculation easier.
-
Construction and Engineering: Accurate measurements are crucial in construction and engineering. Simplifying fractions helps in calculating dimensions, proportions, and material quantities. Imagine calculating the ratio of different materials in a concrete mix; simplification makes the calculations much more manageable.
-
Finance and Budgeting: Understanding and manipulating fractions is essential for handling percentages, discounts, and interest rates. Simplifying fractions simplifies financial calculations, making it easier to compare different options and make informed decisions.
-
Data Analysis and Statistics: Fractions are frequently used to represent proportions and probabilities in data analysis. Simplifying fractions makes it easier to interpret and present data in a clear and concise manner.
-
Science and Research: Scientific measurements often involve fractions. Simplifying fractions helps researchers to accurately interpret and report their findings. This is particularly true in fields like chemistry and physics where precise measurements are crucial.
Beyond Simplification: Understanding Fraction Equivalence
Simplifying a fraction doesn't change its value; it simply represents the same value in a more concise form. 3/170 and 15/850 are equivalent fractions. This concept is crucial for understanding operations with fractions, such as addition and subtraction where we need to find a common denominator.
Common Misconceptions about Fraction Simplification
Several common misconceptions surround fraction simplification:
-
Only Dividing by 1: Some students mistakenly believe that a fraction can only be simplified by dividing both the numerator and denominator by 1. This is incorrect; any common factor can be used.
-
Incorrect GCD Calculation: Errors in calculating the GCD lead to incorrect simplification. Care must be taken to find the greatest common divisor.
-
Not Simplifying Completely: Sometimes, students simplify a fraction but don't reduce it to its simplest form. For instance, they might simplify 15/850 to 3/170 and then fail to notice they could also divide by 1/3. This underlines the importance of checking for further simplification after finding the GCD of the initial numerator and denominator.
Further Exploration: Working with Fractions
Understanding 15/850 and its simplification opens doors to further exploration of fraction-related concepts:
-
Improper Fractions and Mixed Numbers: Improper fractions have numerators larger than their denominators (e.g., 7/4). These can be converted into mixed numbers (e.g., 1 ¾). Understanding this conversion is crucial for various applications.
-
Fraction Operations: Adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing fractions require a solid grasp of fraction simplification. Simplifying fractions before performing these operations often simplifies the calculation process.
-
Decimal Representation: Fractions can be represented as decimals by dividing the numerator by the denominator. Understanding the relationship between fractions and decimals is essential for mathematical fluency.
-
Percentage Conversion: Fractions can be converted to percentages by multiplying the fraction by 100. This conversion is frequently used in real-world applications, such as calculating discounts, interest rates, and expressing proportions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why is simplifying fractions important?
A: Simplifying fractions makes calculations easier, presents data more clearly, and ensures accuracy in various applications, from cooking to engineering.
Q: What happens if I simplify a fraction incorrectly?
A: An incorrect simplification leads to inaccurate results in calculations and misinterpretations of data or proportions.
Q: Can a fraction be simplified more than once?
A: Yes, if the simplified fraction still has common factors in its numerator and denominator, it can be further simplified until the GCD is 1 (meaning the fraction is in its simplest form).
Q: What if the numerator and denominator have no common factors other than 1?
A: If the GCD is 1, the fraction is already in its simplest form and cannot be simplified further. This indicates that the fraction is in its simplest, irreducible form.
Q: Are there any online tools to help simplify fractions?
A: While there are various online calculators, the focus should be on understanding the underlying mathematical principles and practicing the manual simplification process. This builds a deeper mathematical understanding than simply using a tool.
Conclusion: Mastering Fractions - A Building Block for Success
Understanding and simplifying fractions like 15/850 is a crucial skill that transcends the classroom. It's a fundamental building block for success in various fields, requiring not only computational proficiency but also a conceptual understanding of equivalent fractions and the greatest common divisor. By mastering this seemingly simple concept, individuals equip themselves with a powerful tool for problem-solving and critical thinking applicable throughout life. Remember, practice is key – the more you work with fractions, the more confident and proficient you'll become. So grab your pencil and paper, and start practicing!
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 15 Of 850 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.