15 Of 1600
stanleys
Sep 17, 2025 · 6 min read
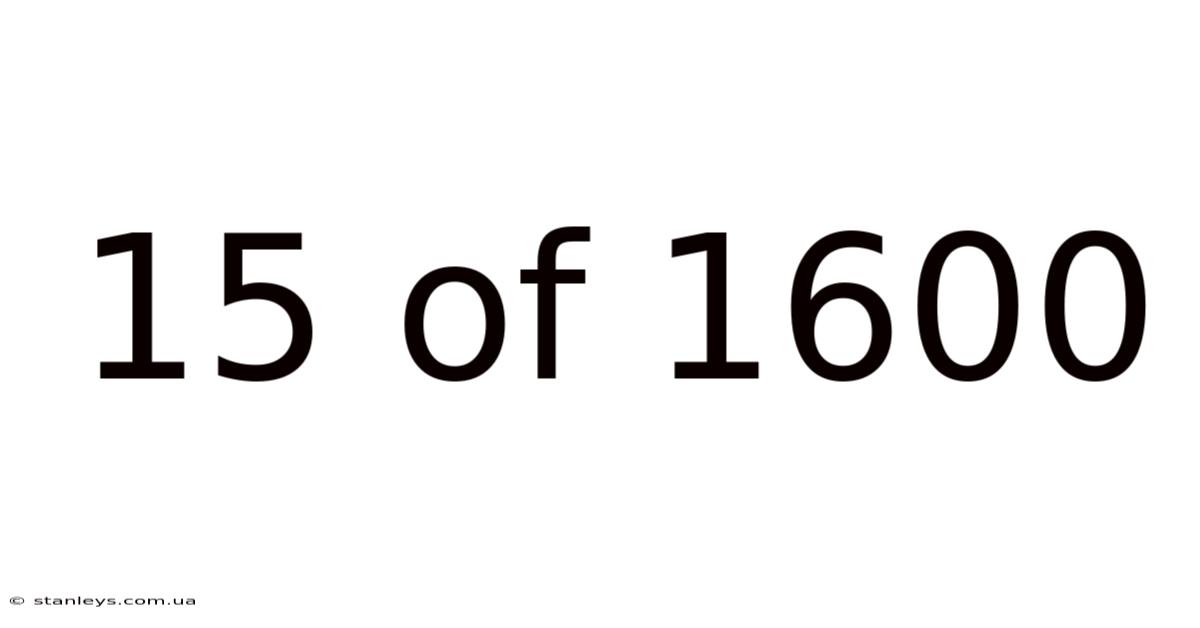
Table of Contents
Decoding the Enigma: Understanding the Significance of 15 out of 1600
The seemingly simple fraction, 15 out of 1600, or 15/1600, holds far more significance than its initial appearance suggests. This ratio can represent a wide range of scenarios, from statistical analysis in scientific research to performance metrics in business, and even probability calculations in everyday life. Understanding its implications requires delving into the underlying context and employing various analytical tools. This article will explore the various ways we can interpret and analyze this fraction, providing practical examples and explaining the importance of context in determining its true meaning.
Understanding the Basics: Ratios and Percentages
Before diving into the complexities of 15/1600, let's refresh our understanding of fundamental mathematical concepts. A ratio is a comparison of two numbers. In our case, the ratio 15:1600 compares the number 15 to the number 1600. This ratio can be expressed as a fraction (15/1600), a decimal (0.009375), or a percentage (0.9375%).
The percentage representation is particularly useful for understanding the relative proportion of 15 within the larger context of 1600. In this case, 15 represents 0.9375% of 1600. This small percentage immediately highlights that 15 is a relatively small component compared to the total of 1600.
Context is King: Interpreting 15/1600 in Different Scenarios
The interpretation of 15/1600 is heavily dependent on the context in which it appears. Let's examine a few possibilities:
1. Scientific Research and Statistical Significance:
In scientific research, a ratio like 15/1600 might represent the number of successful trials out of a total number of trials. For example, if a researcher is testing a new drug and 15 out of 1600 participants experience a significant improvement, this ratio would be crucial in assessing the drug's efficacy. The low percentage (0.9375%) might suggest a lack of statistically significant effect, requiring further investigation and potentially a larger sample size. Statistical tests like chi-squared tests or Fisher's exact test would be necessary to determine if the observed result is likely due to chance or represents a genuine effect.
2. Business Performance and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
In a business context, 15/1600 could represent various metrics. For instance, it might represent the number of defective products out of a total production batch of 1600. A defect rate of 0.9375% might be considered acceptable or unacceptable depending on industry standards and the company's quality control targets. Alternatively, it could represent customer complaints: 15 complaints out of 1600 customers might indicate a relatively low level of customer dissatisfaction. However, the context is key; in some industries, even a small number of complaints could signify serious issues requiring immediate attention.
3. Probability and Risk Assessment:
Imagine a lottery with 1600 tickets. If you hold 15 tickets, your probability of winning is 15/1600, or 0.9375%. This low probability reflects the low chance of winning with such a small number of tickets relative to the total number of entries. Similarly, in risk assessment, this ratio could represent the probability of a specific event occurring. A low probability doesn't necessarily mean the event is impossible; rather, it suggests a low likelihood, aiding in decision-making regarding risk mitigation strategies.
4. Survey Results and Sampling Error:
In surveys, 15/1600 could represent the number of respondents who gave a particular answer out of a total of 1600 respondents. For example, 15 out of 1600 people might have chosen a specific political candidate. However, it's crucial to consider the sampling error or margin of error. The small sample size (15) may not accurately represent the entire population, leading to a potentially unreliable conclusion. Confidence intervals and other statistical techniques are used to estimate the range within which the true population proportion likely falls.
5. Quality Control and Acceptance Sampling:
In manufacturing, 15/1600 might be used in acceptance sampling. Inspecting every single item (1600) might be costly and time-consuming. Instead, a sample (e.g., 100 items) is inspected. If 15 defects were found within that sample of 100, that would equate to a defect rate of 15%. In contrast, if only 15 defects were found in the entire batch of 1600, the defect rate would be significantly lower. This highlights the importance of sample size in determining the true defect rate.
Beyond Simple Interpretation: Deeper Analytical Techniques
While converting 15/1600 to a percentage provides a basic understanding, deeper analytical techniques often provide a more nuanced interpretation. These include:
-
Statistical hypothesis testing: To determine if the observed ratio is statistically significant, hypothesis tests are needed. This involves formulating a null hypothesis (e.g., there's no difference between the groups) and an alternative hypothesis (e.g., there is a difference). The results of the test determine whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
-
Confidence intervals: To provide a range of plausible values for the true population proportion, confidence intervals are constructed. A 95% confidence interval would give a range of values where we are 95% confident that the true population proportion lies within.
-
Bayesian statistics: This approach incorporates prior knowledge or beliefs into the analysis, allowing for a more informed interpretation of the data. Bayesian methods are particularly useful when dealing with small sample sizes like in this case.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How do I calculate the percentage from 15/1600?
A: To calculate the percentage, divide 15 by 1600 and then multiply by 100: (15/1600) * 100 = 0.9375%.
Q: Is 15/1600 statistically significant?
A: Statistical significance depends on the context and the chosen significance level (typically 0.05 or 5%). A hypothesis test is required to determine if the observed ratio is statistically significant. Generally, a very small percentage such as this would suggest a lack of significance unless the context dictates otherwise (e.g., extremely rare events).
Q: What are the limitations of interpreting 15/1600 without more context?
A: Without knowing the context, it's impossible to determine the true significance of 15/1600. It could represent a small but important effect, a negligible finding, or a result with significant implications depending on the application.
Q: How can I improve the reliability of an analysis based on 15/1600?
A: Increasing the sample size is crucial for improving reliability. The larger the sample size, the more precise the estimate of the true population proportion will be.
Conclusion: The Importance of Contextual Understanding
The seemingly simple ratio of 15/1600 demands careful consideration. Its interpretation hinges entirely on the context within which it's presented. While converting it to a percentage (0.9375%) provides a quick overview, deeper analysis, including statistical testing and confidence intervals, is often required to draw meaningful conclusions. Remember, the numerical value itself is meaningless without understanding the underlying scenario and the implications of that ratio within its specific field of application. Therefore, always consider the context before making any conclusions based on this or any similar ratio. Failing to do so can lead to misinterpretations and potentially flawed decision-making.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
69 1kg In Stone
Sep 17, 2025
-
94 8kg In Stones
Sep 17, 2025
-
104f To C
Sep 17, 2025
-
360 X 12
Sep 17, 2025
-
20 Off 44
Sep 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 15 Of 1600 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.