12x X 2
stanleys
Sep 10, 2025 · 6 min read
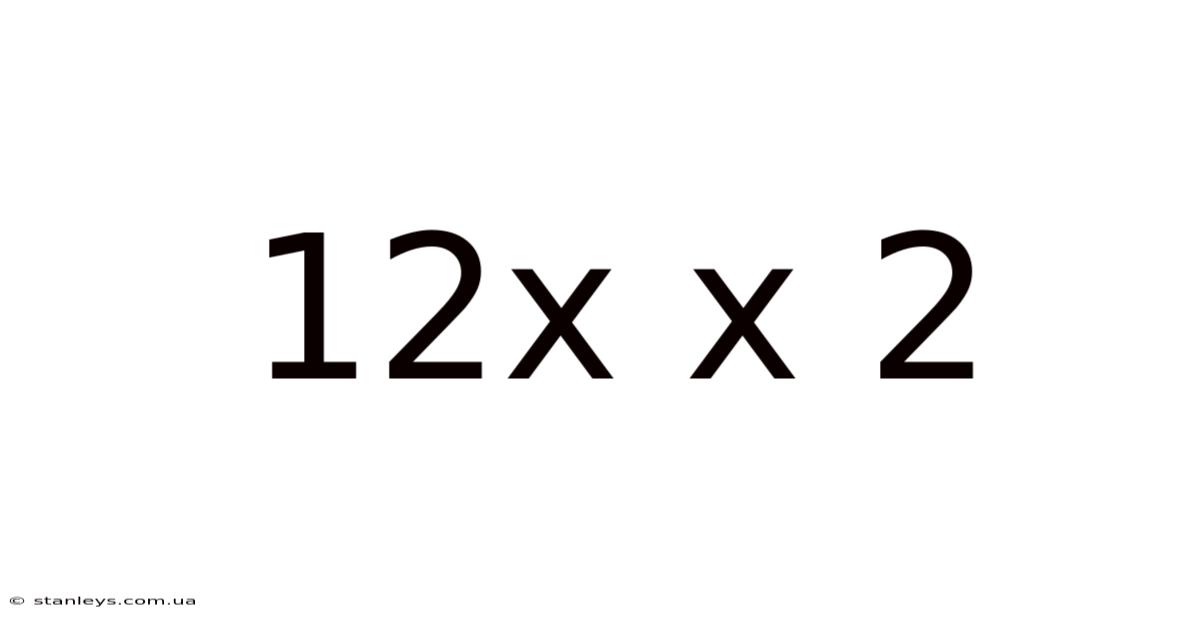
Table of Contents
Decoding 12 x 2: A Deep Dive into Multiplication and its Applications
This article explores the seemingly simple multiplication problem, 12 x 2, delving far beyond the immediate answer. We'll uncover the fundamental principles of multiplication, explore its various applications across different fields, and examine its significance in broader mathematical concepts. This exploration will be accessible to all levels, from elementary school students grasping the basics to those seeking a deeper understanding of mathematical foundations. We'll cover the practical uses, the underlying theory, and even touch upon some fascinating historical context.
Understanding the Basics: What is Multiplication?
Multiplication, at its core, is repeated addition. When we say 12 x 2, we're essentially asking: "What is the sum of twelve added to itself twice?" This simple interpretation forms the bedrock of understanding. So, 12 x 2 = 12 + 12 = 24. This foundational understanding is crucial, especially for younger learners, as it bridges the gap between addition and the more abstract concept of multiplication.
We can represent this visually in several ways:
- Using objects: Imagine 12 apples in two separate baskets. Counting all the apples gives us 24.
- Using a number line: Start at 0 and jump 12 units twice. You'll land on 24.
- Using an array: Imagine a rectangle with 12 rows and 2 columns. The total number of squares represents the product (24).
Different Methods for Calculating 12 x 2
While the direct addition method (12 + 12) is straightforward, let's explore other methods to solve 12 x 2, highlighting the versatility of mathematical approaches:
-
Distributive Property: This powerful property allows us to break down numbers to simplify calculations. We can rewrite 12 as (10 + 2). Then, 12 x 2 becomes (10 + 2) x 2 = (10 x 2) + (2 x 2) = 20 + 4 = 24. This method is particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers.
-
Mental Math Techniques: With practice, we can perform this calculation mentally. Recognizing that 12 is close to 10, we can think: 10 x 2 = 20, and then add the remaining 2 x 2 = 4, giving us 24. This emphasizes the importance of developing mental agility in mathematics.
-
Using a Multiplication Table: The humble multiplication table is an invaluable tool. Locating the intersection of the row for 12 and the column for 2 readily provides the answer: 24.
Applications of Multiplication: Beyond the Classroom
The seemingly simple equation, 12 x 2, finds its application in numerous real-world scenarios:
-
Shopping: If a bag of apples costs $12, and you buy two bags, the total cost is 12 x 2 = $24.
-
Cooking: A recipe calls for 12 ounces of flour per batch. To make two batches, you'll need 12 x 2 = 24 ounces of flour.
-
Construction: If a wall requires 12 bricks per row, and you need two rows, you'll need 12 x 2 = 24 bricks.
-
Time Management: 12 hours x 2 = 24 hours (a full day). This demonstrates the use of multiplication in representing duration.
-
Data Analysis: Imagine a survey where 12 participants each responded twice. The total number of responses would be 12 x 2 = 24.
These examples showcase the pervasive nature of multiplication in everyday life, highlighting its practical utility and relevance.
The Mathematical Foundation: Exploring Factors and Multiples
Understanding the concept of factors and multiples is crucial for grasping the deeper meaning behind 12 x 2.
-
Factors: The factors of a number are the numbers that divide it without leaving a remainder. The factors of 24 (the product of 12 x 2) are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, and 24. Understanding factors helps in simplifying fractions and solving algebraic equations.
-
Multiples: Multiples are the result of multiplying a number by an integer. The multiples of 12 are 12, 24, 36, 48, and so on. Understanding multiples helps in identifying patterns in number sequences and solving problems involving ratios and proportions.
In the context of 12 x 2, 12 and 2 are factors of 24, and 24 is a multiple of both 12 and 2. This connection underscores the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts.
Expanding the Scope: Beyond Whole Numbers
While 12 x 2 involves whole numbers, the concept of multiplication extends to fractions, decimals, and even more complex numbers. Let's briefly touch upon these expansions:
-
Fractions: 12 x 2/3 involves multiplying a whole number by a fraction. We multiply the numerators and denominators separately: (12 x 2) / 3 = 24/3 = 8.
-
Decimals: 12 x 2.5 involves multiplying a whole number by a decimal. We can either convert the decimal to a fraction (2.5 = 5/2) or use the standard decimal multiplication method. 12 x 2.5 = 30.
-
Algebra: Multiplication is fundamental in algebra. The expression 12x represents 12 multiplied by an unknown variable 'x'. Solving for 'x' involves using inverse operations.
Historical Context: The Evolution of Multiplication
Multiplication as a concept has evolved over centuries. Early civilizations used various methods to represent and calculate multiplications. The ancient Egyptians used a doubling method, repeatedly doubling one number until they reached the desired product. The Babylonians used a sexagesimal system (base-60), which influenced our current system of measuring time and angles. The development of algorithms and computational tools has significantly streamlined the process of multiplication, allowing for calculations involving far larger numbers and greater complexity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Is there a difference between 12 x 2 and 2 x 12? A: No, multiplication is commutative, meaning the order of the numbers doesn't affect the product. Both 12 x 2 and 2 x 12 equal 24.
-
Q: How can I make multiplication easier to learn? A: Practice is key! Use visual aids, real-world examples, and different calculation methods to reinforce your understanding.
-
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when multiplying? A: Errors often arise from incorrect place value during multi-digit multiplication and forgetting to carry over numbers. Careful attention to detail is crucial.
-
Q: How does multiplication relate to other mathematical operations? A: Multiplication is closely related to addition, division, and exponents. It forms the basis of many more advanced mathematical concepts.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of 12 x 2
While seemingly elementary, the multiplication problem 12 x 2 serves as a gateway to understanding broader mathematical principles and their applications. From its fundamental definition as repeated addition to its application across various fields, 12 x 2 embodies the power and versatility of mathematics. By understanding the underlying concepts and practicing different methods, we can not only solve simple problems but also develop a strong foundation for tackling more complex mathematical challenges in the future. The journey from understanding 12 x 2 to mastering advanced mathematical concepts is a continuous process of exploration and learning, rewarding those who embrace its intricacies. The seemingly simple equation holds within it the key to unlocking a world of mathematical possibilities.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Short Of War
Sep 10, 2025
-
24kmh To Mph
Sep 10, 2025
-
800 X 5
Sep 10, 2025
-
20 Off 36
Sep 10, 2025
-
10 Of 240
Sep 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 12x X 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.