120 Of 90
stanleys
Sep 17, 2025 · 6 min read
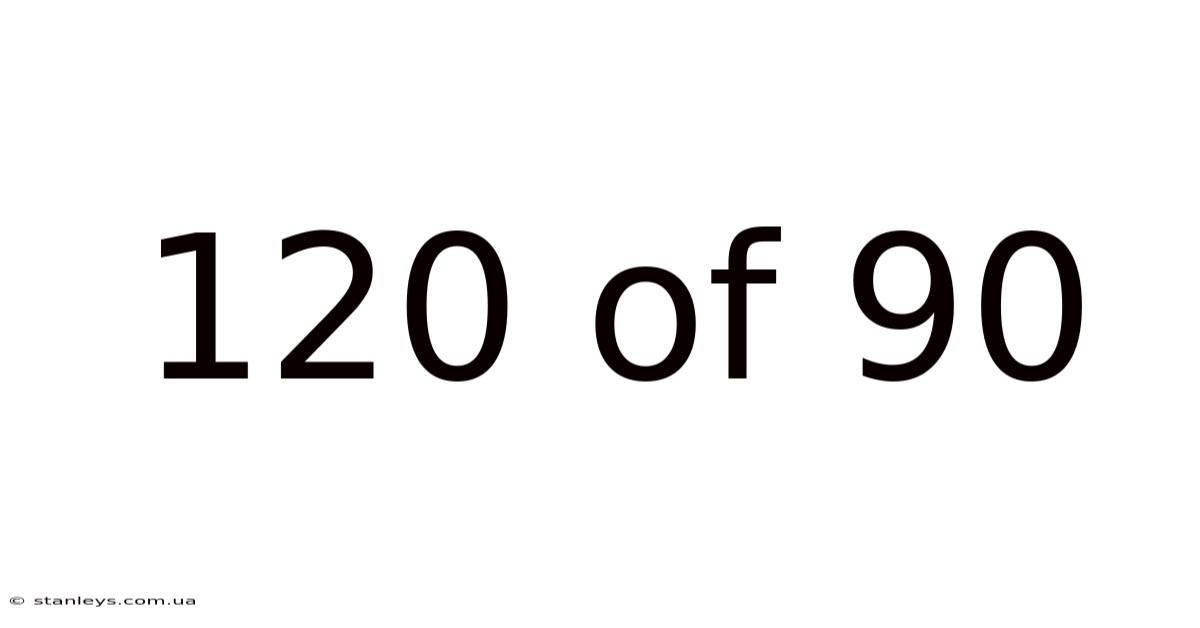
Table of Contents
Decoding 120/90: Understanding Blood Pressure and its Implications
Understanding your blood pressure is crucial for maintaining good health. This article delves into the meaning of a 120/90 blood pressure reading, explaining what it signifies, potential risks associated with it, lifestyle modifications for improvement, and when to seek professional medical advice. We will explore the science behind blood pressure, addressing common questions and misconceptions surrounding this vital health indicator.
What Does 120/90 Blood Pressure Mean?
A blood pressure reading of 120/90 mmHg (millimeters of mercury) represents the pressure exerted by your blood against your artery walls. The top number, 120, is the systolic pressure, reflecting the pressure when your heart beats and pumps blood. The bottom number, 90, is the diastolic pressure, indicating the pressure when your heart rests between beats.
For many years, 120/80 mmHg was considered the ideal blood pressure. However, recent guidelines have shifted this slightly, acknowledging that even a reading of 120/90 mmHg may warrant attention and lifestyle modifications for some individuals. This reading falls within the elevated blood pressure category, meaning it's higher than optimal but not yet classified as hypertension (high blood pressure). However, it signifies a greater risk of developing hypertension in the future.
Understanding the Science Behind Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is a complex process influenced by several factors. The heart acts as a powerful pump, circulating blood through a vast network of arteries, veins, and capillaries. The force of this circulation exerts pressure on the blood vessel walls.
Several factors influence blood pressure:
- Cardiac Output: The amount of blood your heart pumps per minute. A higher cardiac output generally leads to higher blood pressure.
- Peripheral Resistance: The resistance to blood flow in the smaller arteries (arterioles). Increased resistance, often due to factors like plaque buildup in arteries (atherosclerosis), contributes to higher blood pressure.
- Blood Volume: The total amount of blood in your circulatory system. Increased blood volume, often caused by dehydration or certain medical conditions, can increase blood pressure.
- Blood Viscosity: The thickness or stickiness of your blood. Higher viscosity, often associated with high cholesterol or dehydration, increases blood pressure.
- Arterial Elasticity: The flexibility of your arteries. As arteries age and lose elasticity, blood pressure tends to rise.
Potential Risks Associated with 120/90 Blood Pressure
While 120/90 mmHg isn't considered hypertension, it's still a significant risk factor for several health problems. It increases the likelihood of developing:
- Hypertension: Elevated blood pressure significantly raises the risk of progressing to hypertension, a major contributor to heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure.
- Heart Disease: High blood pressure strains the heart, leading to conditions like coronary artery disease, heart failure, and heart attacks.
- Stroke: High blood pressure damages blood vessels, increasing the risk of hemorrhagic stroke (bleeding in the brain) or ischemic stroke (blockage of blood flow to the brain).
- Kidney Disease: High blood pressure damages the kidneys, reducing their ability to filter waste products from the blood. This can eventually lead to kidney failure.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): High blood pressure damages arteries in the legs and feet, restricting blood flow and potentially leading to pain, numbness, and even amputation.
Lifestyle Modifications for Lowering Blood Pressure
Fortunately, many lifestyle changes can help lower your blood pressure and reduce your risk of developing hypertension. These modifications are crucial even if your blood pressure is only slightly elevated.
- Dietary Changes:
- Reduce Sodium Intake: Limit processed foods, fast food, and salty snacks. Aim for less than 2,300 milligrams of sodium per day.
- Increase Potassium Intake: Potassium helps balance sodium levels. Good sources include bananas, sweet potatoes, and spinach.
- Eat More Fruits and Vegetables: Fruits and vegetables are rich in nutrients that support heart health.
- Choose Lean Protein Sources: Opt for fish, poultry, beans, and lentils over red meat.
- Limit Saturated and Trans Fats: These unhealthy fats contribute to high cholesterol and increase the risk of heart disease.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, spread throughout the week. This includes brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces strain on the heart and blood vessels.
- Stress Reduction: Chronic stress contributes to high blood pressure. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption raises blood pressure. If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and significantly increases the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Monitor Blood Pressure Regularly: Regularly checking your blood pressure at home can help you track your progress and identify any concerning trends.
When to Seek Professional Medical Advice
If your blood pressure consistently reads 120/90 mmHg or higher, it's crucial to consult your doctor. They can perform a comprehensive evaluation, identify any underlying medical conditions, and recommend appropriate treatment options. You should also seek immediate medical attention if you experience any symptoms such as:
- Severe headache
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Dizziness
- Blurred vision
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Is 120/90 blood pressure dangerous?
A: While not immediately life-threatening, 120/90 blood pressure is considered elevated and increases the risk of developing hypertension and related health problems. It warrants attention and lifestyle modifications to prevent progression.
Q: Can I lower my blood pressure naturally?
A: Yes, significant improvements can often be achieved through lifestyle changes, including diet, exercise, stress management, and quitting smoking.
Q: What medications are used to treat high blood pressure?
A: Several medications, including diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers, can effectively lower blood pressure. Your doctor will determine the most appropriate medication based on your individual needs and health condition. This section should not be interpreted as medical advice; always consult a physician.
Q: How often should I check my blood pressure?
A: The frequency of blood pressure monitoring depends on your individual risk factors and your doctor's recommendations. If you have elevated blood pressure, you may need to check it more frequently.
Conclusion
A blood pressure reading of 120/90 mmHg is a warning sign. While not immediately classified as hypertension, it indicates a higher risk of developing serious health problems. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, including dietary changes, regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol, you can significantly reduce your risk. Regular monitoring and consultation with your doctor are essential for maintaining optimal heart health and preventing the progression to hypertension. Remember, proactive steps taken today can significantly impact your long-term well-being. Don't hesitate to schedule a check-up with your healthcare provider if you have any concerns about your blood pressure. Early detection and intervention are crucial in managing blood pressure and preventing serious health complications.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 120 Of 90 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.