11/6 As Decimal
stanleys
Sep 21, 2025 · 5 min read
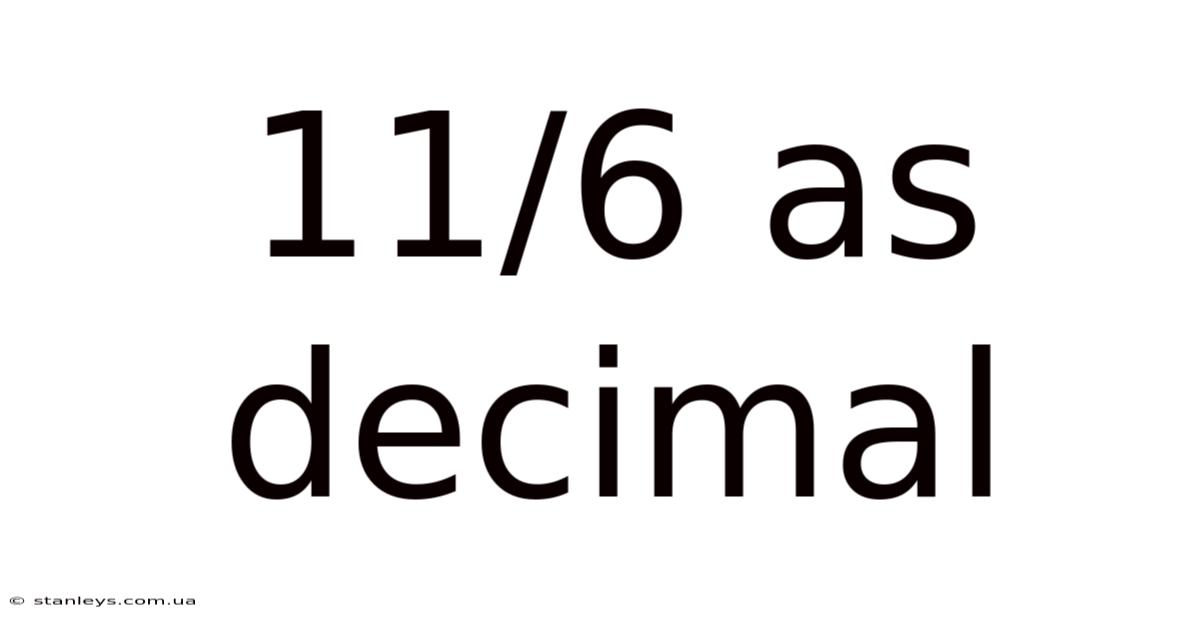
Table of Contents
Decoding 11/6: A Deep Dive into Fraction to Decimal Conversion
Understanding fractions and their decimal equivalents is fundamental to mathematics and numerous real-world applications. This comprehensive guide delves into the conversion of the fraction 11/6 to its decimal representation, exploring the process, its practical implications, and answering frequently asked questions. We'll also touch upon the broader context of fraction-to-decimal conversions and their significance in various fields. This will provide a solid understanding not only of 11/6 as a decimal but also of the underlying principles involved.
Understanding Fractions and Decimals
Before diving into the conversion of 11/6, let's briefly review the concepts of fractions and decimals. A fraction represents a part of a whole, expressed as a ratio of two numbers: the numerator (top number) and the denominator (bottom number). For example, in the fraction 11/6, 11 is the numerator and 6 is the denominator. This means we have 11 parts out of a total of 6 parts.
A decimal, on the other hand, represents a number using the base-10 system. It uses a decimal point to separate the whole number part from the fractional part. For instance, 3.14 is a decimal number, where 3 is the whole number part and .14 is the fractional part.
Converting 11/6 to a Decimal: The Process
Converting a fraction to a decimal involves dividing the numerator by the denominator. In the case of 11/6, we perform the division: 11 ÷ 6.
Using long division:
1
6 | 11
-6
5
At this point, we have a quotient of 1 and a remainder of 5. Since the remainder is not zero, we continue the division by adding a decimal point and a zero to the remainder:
1.8333...
6 | 11.0000
-6
50
-48
20
-18
20
-18
20
-18
...
As you can see, the division results in a repeating decimal: 1.8333... The digit 3 repeats infinitely. This is often represented as 1.8̅3. The bar above the 3 indicates that the digit repeats indefinitely.
Therefore, 11/6 as a decimal is 1.8̅3 or approximately 1.833. The approximation is used for practical purposes when infinite repeating decimals are not suitable.
Understanding the Result: Improper Fractions and Mixed Numbers
The fraction 11/6 is an improper fraction because the numerator (11) is larger than the denominator (6). This indicates that the fraction represents a value greater than one. When converting improper fractions to decimals, the result will always be a decimal number greater than 1.
We can also express 11/6 as a mixed number: 1 5/6. This means one whole unit and five-sixths of another unit. While the mixed number representation is useful in certain contexts, the decimal representation (1.8̅3) provides a more readily usable form for calculations, especially those involving computers or calculators.
Practical Applications of Decimal Representation
The decimal representation of 11/6, or any fraction for that matter, finds numerous applications in various fields:
-
Engineering and Physics: Precise measurements and calculations often require decimal representations for accuracy. For example, in calculating the dimensions of a component or the velocity of an object.
-
Finance: Decimal representation is crucial in financial calculations, including interest rates, currency conversions, and stock prices. The decimal form offers ease in computations compared to fractions.
-
Computer Science: Computers primarily operate using binary code, but decimal representations are used extensively in user interfaces and programming for ease of understanding and input/output operations.
-
Everyday Life: Many everyday situations involve fractional quantities, like measuring ingredients in cooking or calculating distances. The decimal equivalent facilitates easier calculations and comparisons.
Beyond 11/6: Generalizing Fraction to Decimal Conversion
The method used to convert 11/6 to a decimal applies to any fraction. The key is always to divide the numerator by the denominator. The result can be:
-
A terminating decimal: The division results in a finite number of digits after the decimal point (e.g., 1/4 = 0.25).
-
A repeating decimal: The division results in a pattern of digits that repeats infinitely (e.g., 1/3 = 0.3̅3).
-
A non-repeating, non-terminating decimal: These are irrational numbers, like pi (π), which have an infinite number of digits without any repeating pattern.
Different Methods of Conversion
While long division is the fundamental method, other approaches exist, especially for simple fractions:
-
Memorization: Common fractions like 1/2 (0.5), 1/4 (0.25), and 1/3 (0.3̅3) are often memorized.
-
Using a Calculator: Calculators provide a quick and easy way to convert fractions to decimals.
-
Converting to Equivalent Fractions: Sometimes, converting a fraction to an equivalent fraction with a denominator that is a power of 10 (10, 100, 1000, etc.) simplifies the conversion to a decimal. For instance, 3/5 can be converted to 6/10, which is easily represented as 0.6.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Why is 11/6 a repeating decimal?
A1: A fraction results in a repeating decimal when the denominator, after simplifying the fraction to its lowest terms, contains prime factors other than 2 and 5. Since 6 = 2 x 3, the presence of the prime factor 3 leads to a repeating decimal.
Q2: Is there a way to predict whether a fraction will result in a terminating or repeating decimal?
A2: Yes. A fraction will result in a terminating decimal if, after simplification, its denominator contains only the prime factors 2 and/or 5. Otherwise, it will be a repeating decimal.
Q3: How accurate should the decimal approximation be?
A3: The required accuracy depends on the context. For everyday purposes, a few decimal places might suffice. However, scientific and engineering applications often require a higher degree of precision.
Q4: Can I use a calculator to convert fractions to decimals?
A4: Yes, most calculators have a fraction-to-decimal conversion function. Simply enter the fraction and press the equals button.
Conclusion
Converting the fraction 11/6 to its decimal equivalent, 1.8̅3, illustrates a fundamental concept in mathematics with wide-ranging applications. Understanding the process of fraction-to-decimal conversion, the different types of decimal representations (terminating and repeating), and their practical uses provides a strong foundation for further mathematical exploration and problem-solving in various fields. Remember that while calculators are convenient tools, understanding the underlying principles remains crucial for true mathematical comprehension and problem-solving prowess. The ability to convert fractions to decimals, and vice versa, is an essential skill that will serve you well throughout your mathematical journey.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 11/6 As Decimal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.