109 X 3
stanleys
Sep 21, 2025 · 5 min read
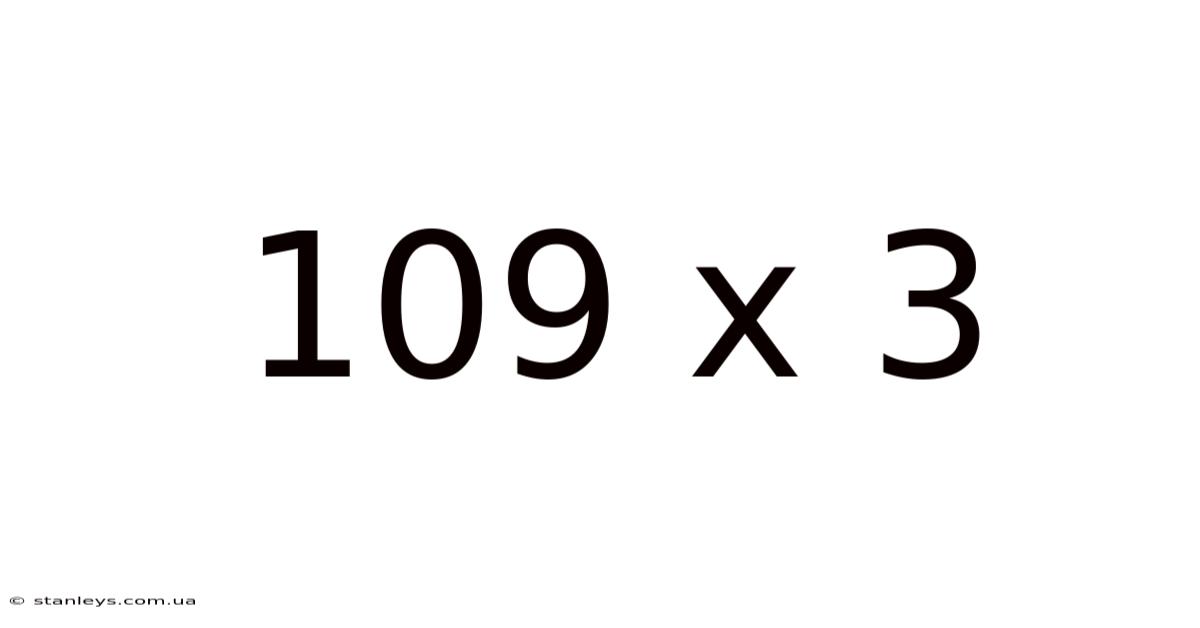
Table of Contents
Decoding 109 x 3: A Deep Dive into Multiplication and its Applications
This article explores the seemingly simple multiplication problem, 109 x 3, but uses it as a springboard to delve into the broader world of multiplication, its underlying principles, various methods of calculation, and its numerous applications across diverse fields. Whether you're a student brushing up on your arithmetic skills or someone interested in the fascinating intricacies of mathematics, this comprehensive guide will provide a detailed and insightful understanding of this fundamental operation and its significance. We will cover everything from basic multiplication techniques to more advanced concepts, ensuring a thorough exploration of this core mathematical concept.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Multiplication
Multiplication, at its core, is repeated addition. When we say 109 x 3, we're essentially asking: what is the sum of three 109s? This can be written as 109 + 109 + 109. While this approach works for smaller numbers, it becomes cumbersome as numbers increase. Multiplication provides a concise and efficient way to handle such repeated addition. The number 109 is called the multiplicand, and the number 3 is called the multiplier. The result of the multiplication, which we will calculate shortly, is called the product.
Methods for Calculating 109 x 3
Several methods can be employed to calculate 109 x 3. Let's explore a few:
1. Standard Multiplication Algorithm: This is the method most commonly taught in schools. It involves multiplying each digit of the multiplicand by the multiplier, starting from the rightmost digit and carrying over any tens or hundreds to the next column.
- Multiply 9 (ones place of 109) by 3: 9 x 3 = 27. Write down 7 and carry-over 2.
- Multiply 0 (tens place of 109) by 3 and add the carry-over 2: (0 x 3) + 2 = 2. Write down 2.
- Multiply 1 (hundreds place of 109) by 3: 1 x 3 = 3. Write down 3.
Therefore, 109 x 3 = 327.
2. Distributive Property: This method breaks down the multiplication into smaller, more manageable parts. We can rewrite 109 as (100 + 9). Then, applying the distributive property, we get:
3 x (100 + 9) = (3 x 100) + (3 x 9) = 300 + 27 = 327
This method highlights the underlying principles of multiplication and showcases its connection to addition.
3. Mental Math Techniques: With practice, you can perform this calculation mentally. One approach involves breaking down the numbers:
- Think of 109 as 110 - 1.
- Calculate 110 x 3 = 330 (easier to do mentally).
- Subtract the 3 that we added earlier: 330 - 3 = 327.
This method demonstrates that efficient calculation often involves strategic manipulation of numbers.
The Significance of Multiplication in Everyday Life
Multiplication is far from a mere classroom exercise; it's a fundamental tool used extensively in various aspects of daily life. Consider these examples:
- Shopping: Calculating the total cost of multiple items (e.g., 3 shirts at $109 each).
- Cooking: Scaling up recipes (e.g., tripling a recipe that calls for 109 grams of flour).
- Travel: Determining the total distance traveled when covering the same distance multiple times (e.g., driving 109 km three times).
- Finance: Calculating interest earned or taxes owed.
- Construction: Calculating the quantity of materials needed for a project.
These examples underscore how deeply embedded multiplication is in our daily routines, often unnoticed but crucial for accurate calculations and planning.
Multiplication in Advanced Mathematical Concepts
Beyond its everyday applications, multiplication forms the bedrock of numerous advanced mathematical concepts:
- Algebra: It is fundamental to solving algebraic equations and understanding polynomial expressions. The distributive property, demonstrated earlier, is a cornerstone of algebraic manipulation.
- Calculus: Differentiation and integration, core concepts in calculus, rely heavily on the principles of multiplication and its inverse, division.
- Linear Algebra: Matrices, which are used to represent systems of linear equations, involve extensive multiplication operations.
- Number Theory: Concepts like prime factorization and divisibility are intimately connected to multiplication.
Exploring Related Mathematical Operations
Understanding multiplication involves appreciating its relationship with other arithmetic operations:
- Addition: As mentioned earlier, multiplication is repeated addition.
- Subtraction: Subtraction is the inverse operation of addition, providing a way to "undo" multiplication in certain contexts. For example, if we know 3 x X = 327, we can find X by dividing 327 by 3.
- Division: Division is the inverse operation of multiplication. It allows us to determine how many times one number is contained within another. In our example, 327 / 3 = 109.
Addressing Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What are some common mistakes students make when learning multiplication?
A1: Common mistakes include errors in carrying over digits, misplacing digits during the multiplication process, and not understanding the concept of place value. Consistent practice and a strong understanding of place value are crucial to avoiding these errors.
Q2: Are there any alternative methods for multiplying large numbers?
A2: Yes, several methods exist, including the lattice method, the box method, and various mental math strategies. These methods offer alternative approaches for multiplying numbers, often suited for different learning styles and situations.
Q3: How can I improve my multiplication skills?
A3: Consistent practice is key. Start with smaller numbers and gradually increase the difficulty. Use flashcards, online resources, and practice problems to build fluency and speed. Understanding the underlying principles, such as the distributive property, can enhance comprehension and accuracy.
Q4: What is the importance of learning multiplication tables?
A4: Memorizing multiplication tables (times tables) is crucial for building fluency and speed in calculations. It automates basic multiplication facts, freeing up mental resources to focus on more complex calculations.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of 109 x 3 and Beyond
The seemingly simple problem, 109 x 3, opens a door to a vast world of mathematical concepts and applications. While the answer, 327, is straightforward, the journey to understanding the underlying principles, alternative methods of calculation, and real-world applications provides a rich and rewarding educational experience. Mastering multiplication isn't just about getting the right answer; it’s about building a foundational understanding of a crucial mathematical tool used extensively in various fields. From everyday calculations to advanced mathematical concepts, the power of multiplication extends far beyond the simple equation we started with. Continuous practice and exploration will not only enhance your mathematical skills but also foster a deeper appreciation for the beauty and practicality of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 109 X 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.